Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
- Created by: amazingemilyjones
- Created on: 10-04-19 19:18
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Cell Structure
- Basic building blocks of life are the same for prokaryotes and eukaryotes
- Lipids
- Nucleotides
- Amino acids
- These make cellular structures and regulate cell physiology. Significant differences exist
- Size, shapes and organisation
- Breaking down cell components
- Genetic structures
- Intracellular and extracellular structures
- Reproductive process
Eukaryotes
- Generally more advanced than prokaryotes. Many unicellular organisms are eukaryotic, all cells in multicellular organisms are eukaryotic.
- E.g. human lymphocyte, human myocyte, yeast/fungi (Candida albicans, Sacchromyces cerevisae)

Prokaryotes
- Unicellular organisms, found in all environments - largest group of organisms due to bacteria which appeared about 4 billion years ago
- e.g. Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli
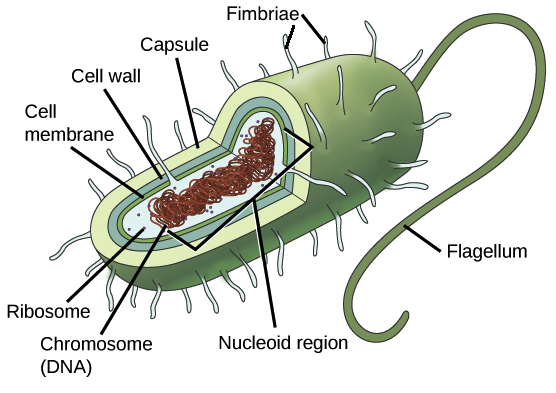
Size and Shape
Characteristics Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Size 0.4-2.5um 3-70um
Shape Spherical, rod, spiral Very varied
Arrangements Groups, biofilm, different Arrange to form
types of bacteria tissue/organs
Different cell types
Genetic Structures
Genetic Structures Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
DNA Single circular chromosome Paired chromosomes
Location Nuclear region (nucleoid) Membrane-bound nucleus
Nucleolus Absent Present
Histones Absent Present
Extrachromosomal Plasmids Organelles -
DNA mitochondria, chloroplasts
Intracellular Structures
Structure Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Plasma membrane No sterols Sterols
Internal membranes Mostly absent Numerous
Endoplasmic reticulum Absent Present
Golgi apparatus Absent Present
Peroxisomes Absent Present
Lysosomes Absent Present
Repiratory enzymes Cell membrane Mitochondria
Ribosomes 70s 70s and 90s
Cytoskeleton Absent Present
Extracellular Structures
Structure Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Cell wall Peptidoglycan Cellulose in plants,
chitin in fungi
External layer Capsule/slime layer Some protists have
pellicle or shell
Flagella Present Present
Cilia Absent Present
Pili Present Absent
Capsules and Slime Layers
- Present in prokaryotes only
- Present in gram postive and negative cells
- Composition
- High molecular weight polysaccharide
- Polymer of amino acids - Bacillus anthracis
- Biofilms/slime layers have implications on human defense mechanisms, e.g. immune system and antibiotics
Cell Division
Reproduvtive Process Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
Cell division Binary fission Mitosis/meiosis
Sexual exchange of No part of Meiosis
genetic material reproduction
Sexual or asexual Asexual only Sexual or asexual
reproduction
Comments
No comments have yet been made