Memory
- Created by: Sophia's spot
- Created on: 01-06-20 15:47
Process of memory
Memory includes three processes:
encoding- putting information into your brain and changing information so it can be stored in the brain
storing- can be stored in long term, short term or sensory (shortest-term element of memory from our senses)
retrieving- accessing information that has been stored in your brain and being able to use it
Process of memory
Encoding
Visual encoding- memories stored by visual cues (seeing)
Acoustic encoding- memories stored by sound (lyrics to a song)
Semantic encoding- stored by knowing the meaning (we know words and how/when to use them)
Process of Memory
Types of Memory: long term
Episodic memory: memory of events and experiences can remember who is there, where it was, how you felt, what you did (birthday party)
Semantic memory: facts, knowledge, and meanings you remember ( Paris is the capital of France)
Procedural memory: muscle memory- remembering how to do things. We remember how to do things without thinking about it. (Driving)
Structures of Memory
Multi-store model

Structures of Memory
Multi-store model description
Sensory- captured by our senses ( when you look at an object the visual image can be remembered at least for a very short time
encoded by senses
Capacity is high
Duration is very short less than a second
Structures of Memory
Multi-store model description
Short term memory
Coding- tends to be acoustic by sound (hearing)
Capacity is limited (5-9 items)
Duration is less than 30 sec unless rehearsed
IMPORTANCE OF REHEARSAL
If the information keeps on being repeated the information will go into your long term memory (maintenance rehearsal)
Structures of Memory
Multi-store model description
Long term Memory
Coding tends to be semantic
Capacity is unlimited
Duration can be up to a lifetime
Structures of Memory
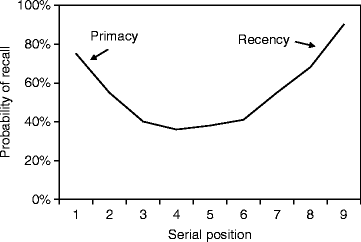
Primacy and recency effect
- words at the beginning are remembered more because they are rehearsed so they are in the LTM
- words at the end of remembered more because they heard recently so they are in the STM
Memory as an Active Process
Reconstructive memory
- people rebuild memory as an active process
- memory is not a process of exact reproduction of experiences
- we record pieces of information and change it to make sense to us in our memory
- culture can affect the storage and recall
- we focus on the meaning of events and make an effort afterward to make sense of fragments of memory
Memory as an Active Process
Effort after meaning
the persistent effort to put unfamiliar ideas into more familiar terms in an attempt to comprehend ambiguous or unfamiliar material.
Factors affecting Memory
Factors affecting Memory
- Inference forgetting may occur if 2 memories compete with each other and similar
- Context is the situation in which something is happening, it can enhance or diminish the accuracy of memory
- False Memory is a memory for something that did not happen but feels as if it were true memory
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Can someone mark this english essay about poppies and remains. »
- Help with gcse poem comparison »
- Are exams just a test of memory? »
- AQA A level psychology »
- Snapchat memories not loading »
- A level psychology »
- PSCYH LITERALLY SO FASt »
- Poppies vs Remains Comparison - Please help! »
- (Computer Science) Difference between MAR and PC? »
- difference between PC and MAR at GCSE level? »
Comments
No comments have yet been made