principles & theories of learning
- Created by: echubb26
- Created on: 06-01-21 12:57
theories of learning
cognitive- new to learning skill needs instruction to understand, will make erros
autonomous- performs skill withought concious though/able to focus on other factors
associative- athlete has progressed from thinking about skill
learning theories
Skinner theory- operant conditioning the use of positive reinforcement to ensure correct repsonses
trial and error, shapes behaviour, manipulates enviroment
reinforced actions strengthend & incorrect actions weakened using the theory of satisfier.
observation kearning- Bandura auggests both acceptable and unacceptable behaviour can be learnt by watching & copying
attention-retention- motor production- motivation
social development theory- Vygotsky
inter-psychological learning- from others externall intra-psycholgical learning- others knowledge
constructivism of a skill by using inter & intra learning to allow assesment of performance
Insight learning (Gestalist theory)
using experience and understanding solve problems relating to skill. use existing knowledge to form idea of general sporting situation
Psychological influences
personality- 'unique psychological make up, individual personality profile affect techniques linked to competitions and training.
Nature VS Nurtue- characteristics controlled by genes affecting individuals whhilst nurture is the affect if enviroment
Trait theory- individuals are born with traits/characteristics, attempts to predict behaviour in comparioson to personality. (introvert/extrovert)
The social learning approach- behaviour is learnt from significant others by socialisation.
observe- identify- reinforce- copy
Interactionist perspective- combines traint and social learningto predict behaviour in situations. influenced by genetic and enviromental factors.
The Lewin- B=F(P*E) behaviour is function of personality & enviroment
Hollanders model 1971- core beliefs- typical response- role related behavior
attitudes
-formed by association with others, can become conditioned by success & reinforced behaviour
C cognitive- representing beliefs
A affective- concerns feeling/emotion
B behavioural- reflects what you do
attitude change- congitive dissonance, new info cause unease/motivate change
persuasive communication, reduce resistance in attitudes (higher authority)
arousal
drive theory- arousal increases as does performance (in linear relation)
inverted U theory- increased arousal improves performance to a optimum arousal to a certain level then performance deteriorates
catastrophe theory-increased arousal improves performance to an optimum point then there is a dramatic reduction in performance.
zone of optimum functioning- ultimate intrinsic experience from a positive mental attitude. these zones change dependant on athlete and sport nature
anxiety
-negative reaction to stress, characterised by nerves, worry & apprehension activated by arousal.
TYPES
congitive- thinking
somatic- body repercussions due to stress
competiticve trait- characteristics
competitive state
measuring anxiety- observations, self report assesment (****), physiological testing ie heart monitior
aggression & assertion
aggression- form of behaviour directed to harm/injure somebody,
hostile aggresion- is intent to cause harm outside of rules
assertive behaviour- act with no intention to harm, no rules broken
causes; pressure, poor officating, history, provoked, loosing, rilvary, nature of sport, arousal, crowd.
agression theories
instinct theory- aggresion is innate, ernergy needs releasing
not reliable= aggresion is learnt, athletes not aggressive off pitch, no proof
Frustration-hypothesis- triggers frustration as a drive leads to aggression
not reliable= not all frustration leads to aggression, not all aggression from frustration
cue arousal- a stimulus triggers arousal, frustration increases arousal but aggression only occur with a cue
social learning- aggression is learnt, if actions are reinforced they are learnt and copied
motivation
intrisic motivation- behaviour driven by internal rewards
external motivation- behaviour driven by external rewards
tangiable- physical thing able to touch
intangiable- not able to physically touch, an accomplishment or sense of achievement
social facilitation- positive effect presence of spectators has on athletes play
social inhibition- negative effect presence of spectators has on athletes play
Zajonc model
attribution theory
weiner's model- 
learnt helpleness
- belief that faliure is inevitable
general- 'i am bad at everything'
specific- 'i am bad at a specific skill'
coaches want to develop mastery orientation- ability to see success blame effort in contrast to learnt helpleness laming ability.
confidence
- belief of an individual about their ability in sport
self-effiacy- self confidence in specific situations
self-esteem- feelings of self worth determined how valuable you feel
Vealeys model of sports confidence
Banduras model of self efficiacy
Leadership
-someone influencing others helping them achieve their goals
prescribed leader- appointed by outside the group, higher authority
emergent leader- appointed from within an existing group
style of leadership
autocratic approach- leader makes decisions, task oreintated style
democratic approach- leader seeks consultation from group
laisse-faire style- leader does very little, leaves group to own devices.
fiedlers contingency model of leadership
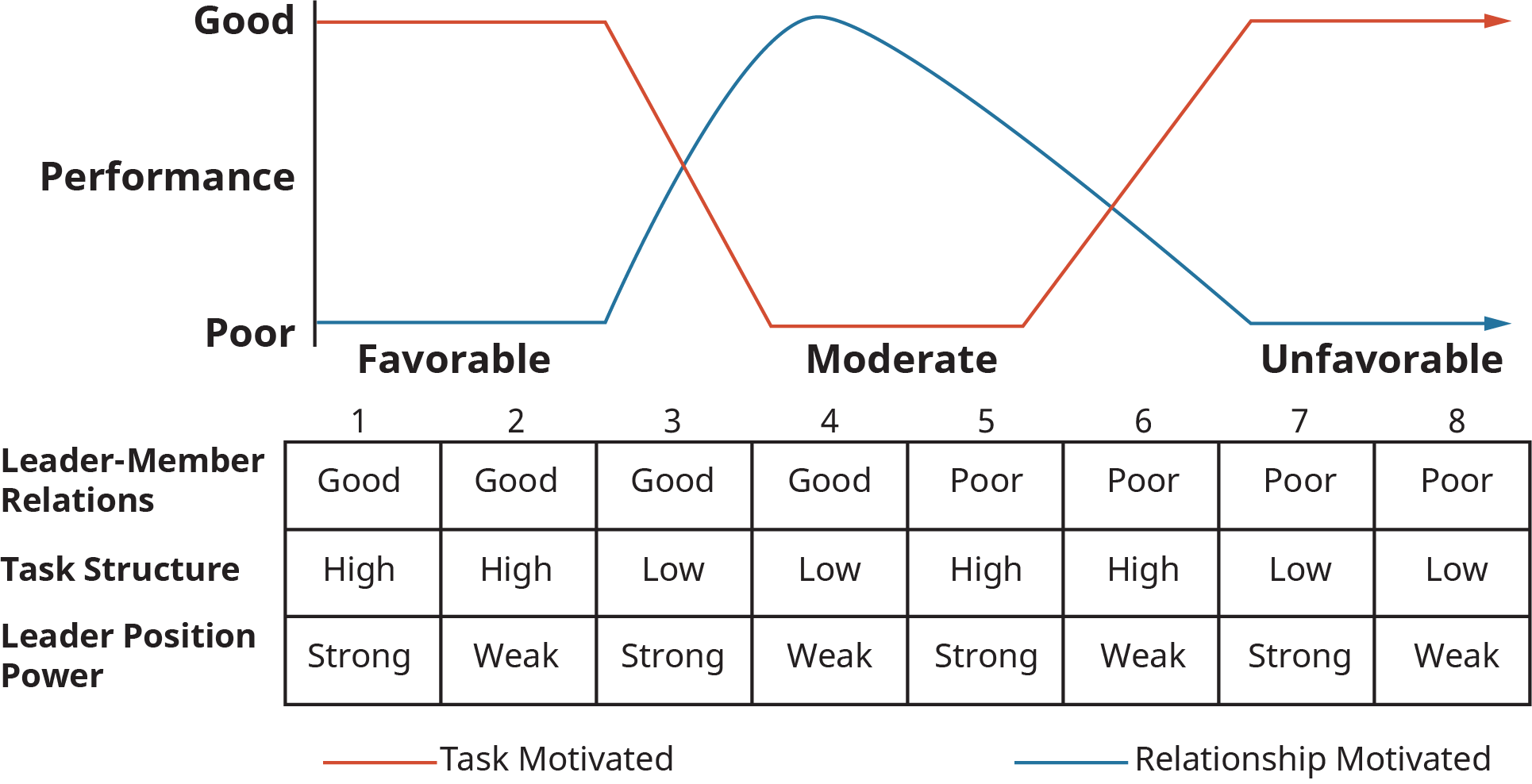
Chelladuras multi dimensional model
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Access course or alevel »
- How do I memorise/learn derivations for engineering »
- Intercalation application: Work experience/clinical placement »
- Personal Statement- Sports Science »
- MSc choice »
- BTEC H&S Care Unit 5: Meeting Individual Care and Support Needs Work Explained »
- Psychology Question AQA »
- Apprenticeships vs University »
- Health and social btec »
- Answering Questions: What is CDIO? »
Comments
No comments have yet been made