Aperture: a hole in optics through which radiation travels (a gap)
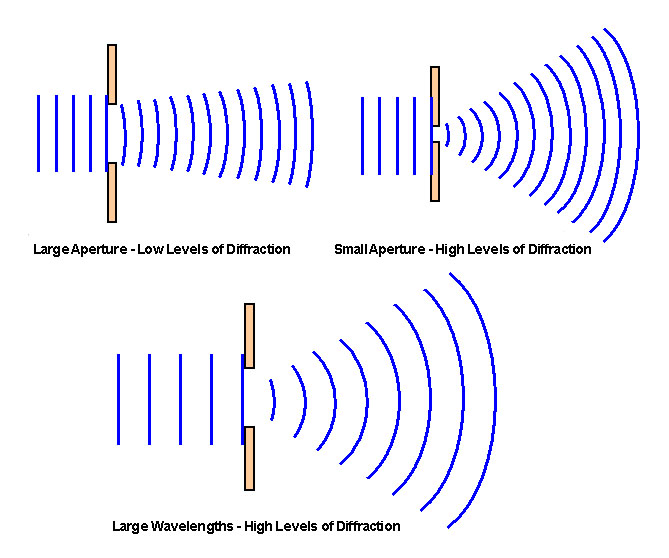
Narrow gap/longer wavelength makes a longer wavelength
When: gap < wavelength, max. defraction ; gap = wavelength, little defraction ; gap > wavelength, no defraction
High levels of defraction produces blurry images and so telescopes should have as large an aperture as possible to produce sharp images
Diffraction grating: set of narrow evenly spaced parallel lines on a thin sheet of glass. Different colours emerge at different angles to produce several spectra
Comments
No comments have yet been made