Nucleic acids
- Created by: Fredcatley
- Created on: 29-11-18 12:22
Structure of nucleotide as a monomer
- Nucleotides are made up of 3 biological molecules that are bonded together with covalent bonds formed by condensation reactions
- The subunits are:Pentose (5C) sugar molecule: ribose or deoxyribose, Organic nitrogenous base: adenine, cytosine, gaunine, thymine or uracil and a Phosphate group.
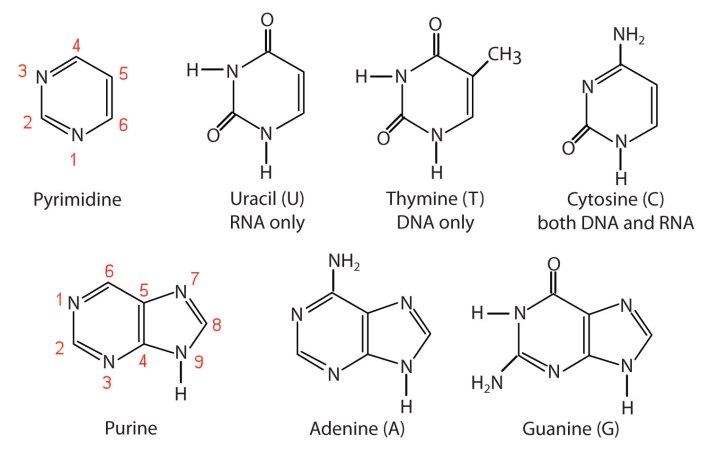
- DNA contains bases: A, C, G, T
- RNA contains bases: A, C, G, U

Organic bases
- Two types of organic bases: purines and pyrimidines
- Purines: 2 carbon-nitogen rings
- Pyrimidines: 1 carbon-nitrogen-ring
Structure of DNA- polynucleotide
- Nucleotides are joined together by condensation reactions to form a polynucleotide chain.
- Phosphate group of 1 nucleotide is joined to the sugar molecule of the next nucleotide in the chain
- 1 polynucleotide foms one of the two-suga phosphate backbones of the DNA molecule

DNA- the nucleic acid
- The nucleic acid forms when two polynucleotides join together by H bonds between nitogenous bases.
- Bases always pair: pyrimidines pair with purines=complementary base pairing
- In DNA: adenine pairs with thymine by 2 H bonds, gaunine pairs with cytosine with 3 H bonds
- The two polynucleotides= antiparallel- run in opposite directions

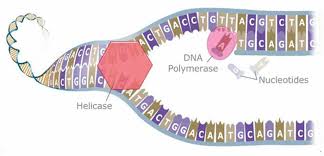
DNA semi-conservative replication
1) Double helux unwinds and is unzipped by helicase which overcomes the H bonds between bases.
2)Two seperate strands act a template for new DNA molecules: new DNA nucleotides are attached to exposed bases that they are complementay too by H bonds.
3)Dna polymerase catalyses the condensation reaction to covalently bond each nucleotide to the adjacent one along the backbone.
4)Two identical DNA copies have now been made: each copy has 1 strand of the original DNA and 1 strand of the new nucleotides (semi-conservative replication).
The genetic code
- Code for DNA is a triplet code in which 3 bases code for an amino acid.
- 20 dif. amino acids and 64 different combinations of triplets
- May be up to 6 codes for the same amino acid: advantageous because if a mutation causes a base change, the triplet may still code for the same amino acid, thus protein produced is not changed.
Protein synthesis: transcription
- When cell needs to produce a protein from a gene RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and unzips the two strands.
- RNA polymerase moves along the template strand in 3' to 5' direction.
- As it moves along it pairs free RNA nucleotides with the complementary nucleotides on the DNA template stand.
- These RNA nucleotides are then covantly linked with phosphodiester bonds to create a polynucleotide chain: 5' to 3' direction, known as mRNA
- mRNA will have the same sequence of nucleotides as the DNA template strand because it has been formed by complementary base pairing with the DNA template strand.

Protein synthesis: translation
- mRNA leaves the nucleus via nuclear pores for the ribosomes, where it acts as a template for proteins to be synthesised.
- Eac triplet is called a codon.
- There are different tRNA molecules for each amino acid, so they pick up the correct amino acid and carry it to the correct position on the mRNA template.
- On the opposite end of the tRNA is an anticodon, which is a triplet that is complementary to the mRNA codon. This ensures that the amino acids are correctly sequenced along the mRNA.
- The ribosome reads the code of a codon at a time. Each amino acid is then attached by a condensation reaction to form a peptide bond with the next amino acid.
- The ribosomes move along the chain and hold the tRNA in place by temporary hydrogen bonds that break once the peptide bond is formed, which allows the tRNA to collect another amino acid and the ribosome to move along the chain.
- The process continues unitl the chain of amino acids is complete and a primay protein structure is formed.
Comparing features of DNA and RNA
Feature DNA RNA
Shape double strand single strand
Type of pentose sugar deoxyribose ribose
Helical nature of the molecule Double helix Single helix
Types of molecules 1 type of DNA 3 types of RNA:
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Role Long term storage protein synthesis
of genetic info
Comparing the roles of DNA and RNA
Features of DNA RNA
the role
Info code Base sequence used to make proteins Copies the DNA
Replication Complementary base pairing Transcription
Size of molecule Strand is very long; more info stored small amounts of info can be copied;molecule is much shorter
Stability of molecule Stable:covalent bonds+double helix Less stable: easily formed+broken
Copying info Code can be unzipped and read due to H bonds between bases of DNA
H bonds and mRNA mean exact copy is formed
DNA precipitation
- DNA precipitation: isolating DNA from cells
- Marmar preparation is a method used:
- 1) Cells disrupted by breaking cell+nuclear membranes using a concentrated detergent solution
- 2) Filtering the resulting suspension removes cell debris+membrane fragments, leaving the soluble proteins+DNA.
- 3)Protease enzyme used to remove the protein leaving only the DNA.
- 4) The DNA can be precipitated using ice cold ethanol.
- 5) Results in a white precipitate being formed, can be used for analysis.
Related discussions on The Student Room
- 25 marker essay biology »
- HELPPPP!!! DNA replication & transcription »
- OCR BIOLOGY PAPER 3 Predictions? »
- Biology Paper 2 AQA Triple Higher 2023 »
- DNA mcq »
- Biochemistry undergraduate course »
- What is DNA repair »
- GCSE English Language Speech Opinions »
- OCR A A-Level Biology Biological Diversity [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- biology aqa alevel amino acid question »
Comments
No comments have yet been made