Migration, Identity and Sovereignty Case Studies
- Created by: Airose
- Created on: 09-05-18 15:42
Internal Migration in China
- Rural to urban migration.
- 1980 80% lived in rural areas, 2012 51%.
- The hukou system tried to prevent migration.
- The Hukou System
- Introduced in 1950s.
- States everyone must be registered to an official residence.
- Hard for migrants to change registration to new location.
- Need a permut to change which is expensive.
- The system favours the rich and wealthy.
- Criticised for beng too restrictive as the manufacturing sector relies so much on migrant workers.
The EU Schengen Agreement
- Began in 1995.
- Abolished mny of the internal boarder controls within the EU.
- Enables passport free movement across most EU member states.
Advantages
- Millions of EU citizens have moved freely.
- Helped to fill job vacancies.
- Reduces expensises of boarder control.
- Reduces time to cross Europe.
Disadvantages
- Allows for free movement of criminals or terrorists.
- Gives easy access to cheap labour, loweing wages.
- Some people don't necessarily want to allow everyone into their country with little to no scrutiny.
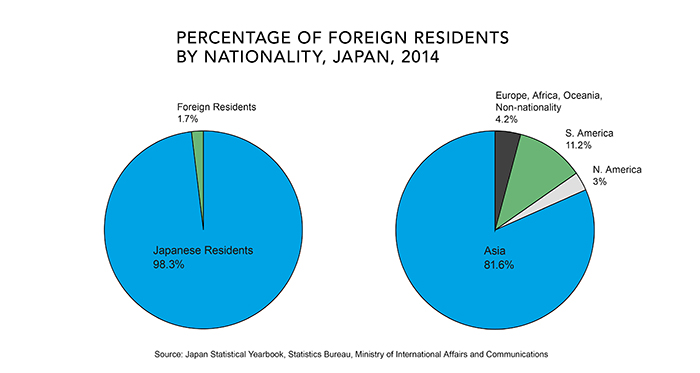
Japans International Migration Policy
- Japans policy is falling with only 27% over 65.
- Only 1.7% of the population are immigrants.
- The culture s based on a homogeneous population.
- A poll in 2014 revealed that the Japanese people beleived the way to solve the crisis is to encourage more women into the workforce not migrants.
- Also developing robotics to fill labour shortages.
- UN suggests Japan needs 17 million immigrants by 2050 to maintain its population.
- However Japanese is not a global business language.
- Japan has a very closed door policy.
- Little evidence this will change.
Australia's International Migration Policy
- For 40 years Australia's policy has been skill based.
- 70% of immigrants are accepted based on skills shortages where there are insufficient Australian workers.
- Australias immigrants each contribute 10% more per capita to the GDP per year than non-immigrants.
- Migrants tend to be younger.
- 88% under 40 and 50% aged 20-34.
- Migrants are used to offset the ageing population.

Singapore's International Migration Policy
- Great cultural diversity.
- Due to it having a past of being a British colonial port.
- Also due to it being the worlds 4th largest financial centre.
- Many global businesses have their head offices there so the workers also relocated.
However there are restrictions on migrants:
- The termination of employment means the migrant must leave in 7 days.
- They also need regular AIDs and HIV tests.
- They cannot marry Singaporeans without the approval of the controller of work permits.
- Female work permit holders who become pregnant are returned home.

UK's Changing International Migration
- UK has 2 main sources of international migrants.
- These are the commonwealth and the EU.
- 1945 after the war there was a shortage of labour in the UK so they encouraged Afro-Caribbean, Indian and Pakistan people to move and fill these gaps.
- The EUs Maastricht Agreement in 1992 increased migration.
- The UK is the EUs second largest economy with the worlds foremost business language so migration high.
Crossing the Mediterranean
Source Countries
- Syria, Iraq, Afganistan, Nigeria, Sudan and more.
Causes of Migration
- Syria- War, ISIS, Instability
- Iraq- War, persecution
- Afganistan- War
- Nigeria-Poverty (70% live below poverty line)
Why Europe?
- Peace
- Better economic prospects.
- Friends and family already moved there.
Top Destination = Germany
Country per capita receiving most migrants = Sweden
Britain's Successful Assimilation of Cultures
- There is no evidence that Muslims are less likely to think of themselves as British than other groups.
- Among those who were born in Britain, over 90% of all groups of whatever religion or ethnicity, think of themselves as British.
- The longer immigrants remain in Britain, the more likely they are to think of themselves as British.
- Immigrants from poorer and less democratic countries assimilate faster into a British identity.
- Immigrants from Pakistan and Bangladesh assimilate into a British identity much faster than those from Western Europe and the United States..
- Ethnicity has a somewhat larger effect on British identity than religion.
- All non-white ethnic groups report lower levels of British identity.
Germany's Poor Assimilation of Cultures
- A third of all children born in Germany belong to immigrant families, but many immigrants are poorly integrated into German society.
- Turks in particular fare poorly.
- An alarmingly high percentage of immigrants have poor prospects of a decent education and career advancement.
- The country need immigrants due to low birth rates and an ageing population.
- The failed immigration is already costing the country up to €16 billion ($20 billion) per year.
Mexico - USA Migration Impacts
Economic
- Cities with high unemployment say Americans should be given the jobs rather than migrants.
- Illegal immigrants work long hours for little money.
- Illegal immigrants dont pay tax and send remittance payments.
Demographic
- 1/5 of the population is now Hispanic.
- Youthful migrants help offset ageing popualtion.
- Higher birth rates of migrants is changing the ethnic population.
Social
- Creates tension which increases hate crime.
- Large number of unaccompanied children at border who later go into care system.
- Culturl erosion
- Media sometimes changes their content to suit migrants as an audience e.g. Netflix adding more Spanish shows.
Iceland's Monoculture
- Only 8.9% of the population were born overseas.
- Wanted to be monocultural.
- Have strict laws to protect this:
- All childrens names must be chosen from an approved list to protect the language.
- The national phone book lists people by first name because most iceland surnames are the farther's name ending in by son boys and dottir for girls.
- The Icelandic language has remained unchanged since 870AD.
- 74% of Icelanders belong to the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Iceland.

Singapores Multiculturalism
- Used to be a British colonial trading post.
- Out of todays population:
- 74% are Chinese decentends
- 13% Malay
- 9% Indian.
- The Singaporean government has tried to create national identity based on Asian values but failed.
Rwanda's Problems with Colonial Rule
- Before the Berlin conference Rwanda had been a unified region home to Tutsi, Hutu and Twa people.
- Tutsi were in control but problems were resolved through a council of elders that included all groups.
- After the Berlin conference Germany established colonial rule over Rwanda.
- After Germanys defeat after the first world war Belguim took control over Rwada.
- The Belguims favoured the Tutsi.
- 1926 they introduced ethnic identity cards to differentiate between the Hutus and Tutsi.
- Rwanda gained independence in 1962 when the Hutus rebelled against the Belgian and Tutsi elite.
- Thousands of Tutsi fled as there was mass killings off them in the 1960 and 70s.
- During the 70s and 80s the Hutus were given the best jobs in public services and military.
- April 1994 the president of Rwanda was killed.
- This led to the genocide of 800,000 Tutsis and moderate Hutus.
- The UN Security Council established an international tribunal to oversee prosecution of suspects involved in the genocide.
Crimea's Contested Boarder
- Crimea has a varied population with 58% ethnic Russians and 24% ethnic Ukrainians.
- Crimea became part of the Russian empire in 1783.
- 1954 it was transferred to Ukraine. Both Russia and Ukraine were Soviet republics.
- in 2014 Ukraines pro-Russian president was removed from power iand replaced with a pro-western government.
- The government wanted membership to the EU and NATO.
- In response Russia seized control of Crimea.
- The Russian speaking majority voted to join Russia in a snap referendum that was considered illegal by the Ukraine and the West.
- 850,000 Ukrainians fled Crimea as a result.

Taiwan's Contested Boarder
- Since the 1950s Taiwan has been independent.
- However China still claims soverignty over it.
- They claim it as a rebel provnce that should be united with the mainland.
- China insists countries should not have official formal relations with both China and Taiwan.
- Means Taiwan has few formal ties with other countries.
- However Taiwan is still an economic success and a top producer of computer tec.
- In 2016 it elected its first female president who is persuing independence.

Rise of Nationalism in India
- India looked for independence from Britain from the beginning of the 20th century.
- After the first wold war India was promised indpendence for help in the war.
- Ghandi was the main leader of this movement.
- Took advantage of post war chaos to blame Britain as the cause of Indias trouble.
- Gained massive support.
- There was conlict such as the Amrisar massacre in 1919 when british troops opened fire on unarmed protestors.
- India became independent in 1947.

Sudan - Costs of Disintegrating Empires
- The major European nations agreed Africas boarders and which country would control each country in the 1884-5 Berlin conference.
- Sudan was divided into north and south territories based on ethnic characteristics.
- Britain modernised the north and abandoned the tribal south.
- This pitted the Sudanese people against each other as the north prospered more.
- 1956 Sudan gains independence.
- 2013 civil war began when the south of Sudan voted to leave Sudan.
- The civil war was one of Africas longest running conflicts
- Tens of thousands had to leave homes.
- Food supplies cut off.
- UN agancies declared a famine that affected over 1 million people.
Cayman Islands as a Tax Haven
- 3 neighbouring Caribbean islands.
- They are a financial honey pot as theyhave a 0% personal income tax and low corporation tax.
- Among the worlds most successful financial centres with over 100,000 registered companies.
- Financial services generate 55% of the islands GDP.
- One of the worlds largest offshore financial centres.
- 40 of the worlds top investment banks and insurance companies are licensed here.
Bolivia Reducing Inequality
- In 2006 President Evo Morales was elected to undo 20 years of privatisation and the influence of IMF.
- Morales belives that privatisation only benefits TNCs.
- The National Coalition for Change (COLANCAM) in 2007:
- Wanted to nationalise resources with profits going to government not TNCs.
- Reduce primary exports to boost domestic manufacturing.
- Redistributed wealth by guaranteeing prices for food products.
- Nationalised the oil and gas industry (before TNCs claimed 82% of their value).
- Bolivia benefitted from increased gas connections, electricity and telecommunications.
- Improvements to healthcare, education, pensons and salaries.
- Reduced wealth inequalities and government debt.
- Morales was elected again in 2014.

Vietnam - Cost of Disintegrating Empires
- Vietnam was a French colony.
- Much of the land was converted into plantations producin rubber, coffee, tea, rice and tabacoo for expots for the colonial power.
- Society was divided into those with land and those without.
- The landless class worked on the landowners planations with little food, healthcare and ducation.
- After 1945 Vietnamese nationalists challenged French rule.
- After a French defeat in 1954 the USA became concerned about the spread of communism in southeast Asia.
- Vietnam was divided into two.
- The Vietnamese nationalists who were supported by a communist China in the Noth.
- The south became an independent non-communist region supported by the USA.
- A long war endured as the nationalists wanted to unify vietnam under their control.
- 1-4 million vietnamese were killed.
- 58,220 Americans wer killed.
- 1975 the south was defeated and an independent united Vietnam was created.
UK and Commonwealth- Migration and Colonial Ties
- After the second world war there was a labour shortage in Europe.
- 1948 the British Nationality Act gave all commonwealth people the right to British citizenship.
- This meant they could now legally settle in the UK and could fill urgant job vacancies.
- Most migrants came from the Caribbean, India and Pakistan as they were well educated.
- They are known as the Windrush generation.

Africa's Rise of Nationalism
- Before 1960's Africa was still under European control.
- However by 1970 most has independence.
- Ghana was the first colonised country to have independence.
Factors Causing the Rise
- After the war most powers lacked money to maintain colonies
- Emergence of new superpowers such as the USA replaced old ones.
- Increased colonial education.
- The Second World War also encouraged African nationalism. Trained some East Africans on how to use guns, exposed them to military weakness of the whites and also exposed Africans to ideas of democracy from American soldiers.
- The formation of the United Nations in 1945 favored African nationalism.
- The formation of political parties also encouraged nationalism in East Africa.
Bosnia- Direct military involvement by UN
- In 1993 the UN was provoked into action by allegations of ethnic clensing by Bosnian Serb forces against Bosnian Muslims.
- To protect Bosnian Muslims the UN designed a safe zone in a small town to the north-eastern of Bosnia.
- This town was protected by Dutch UN peacekeepers.
- The town was soon put under seige by Bosnian serb forces.
- Supplies of food ran low and many starved.
- 1995 the Serb forces captured the town and massacred 8000 Muslim men and boys.
- 23,000 women and chidren were deported.
- Many of the women had been *****.
- Some of the Dutch peacekeepers were captured and threaterned with execution if the Dutch intervened.

Iran- UN Economic Sanctions
- There was a suspicion that Iran was attempting to build nuclear weapons.
- This led to the UN imposing economic sanctions and financial restrictions on Iran in 2012.
- At the time Iran was the 4th largest oil exporting country.
- This meant that they influenced global prices through OPEC.
- The amount of oil that Iran exported massively reduced during the next few years.
- However Irans GDP only fell by 5%.
Crimea- Unilateral action against Russia
- 2014 seized control of Crimea.
- In protest in 2014 the USA, EU, Australia, Canada and Norway all imposed sanctions on 23 leading Russian politicians.
- The politicians overseas financial assets were frozen and they were preventing from travelling to these 5 areas.
- The USA also led moves towards sectoral sanctions ( targeting key areas of the Russian economy such as energy or banking.)
- The UN general assembly met in 2014 but not all UN members wanted further action.
- Sanctions were strengthened.
- However EU members were reluctant to go too far due to their reliance on Russian gas and oil.
Impacts
- US $70-90 billion left Russia as wealthy Russian investors sought secure overseas banks.
- Russian currency was devalued and its international credit rating reduced.
- Russia retaliated by banning imported food from the EU and USA.
- Russia became less dependent on gas and oil exports so diversified its economy.
- Russian farmers gained larger home markets due to restrictions on imported food.
- EU kept importing Russian energy supplies despite sanctions.
UK - Proposed Unilateral Action against Syria
- In 2013 the UK government sought a resolution of the UN Security Council.
- Was to be against the Syrian government forces for the use of chemical weapons.
- However it required backing from all five members.
- Russia and China have a history of vetoing action against Syria so not likely to pass.
- The UK government argued that it had a legal basis for humanitarian intervention to relieve suffering by deterring further use of chemical weapons.
USA Unilateral Action against Iraq
- After the 9/11 attack in 2001 the USA led a coalition force and invaded Iraq.
- This coalition was made up of the USA, UK, Australia and Poland.
- Invaded in 2003 and deposed Saddam Husseins government.
- The UN initially supported the invasion but then disagreed with it.

Uganda and HIPCs initiatives
- In 1992 Uganda's debts totalled US $1.9 billion and was unable to repay these.
- In 2000 it was one of the first countries to benefit from the debt write-offs by the IMF and World Bank through the HIPCs initiative.
The impacts were immediate:
- Government spending rose by 20% ( 40% more on education 70% more on healthcare.
Free primary schooling was introduced so 5 million extra children could go to school.
Enrolement rates went from 62% before the relief to 93% in 2015.
Before the relief 20% more boys than girls went to school. In 2015 the difference was 2%.
The percentage of people undernourished went from 24% to 19% (immediately after).

Regional Migration in UK
- Movement is unrestricted.
- In 2011 12% of the UK population had a different address to the year before.
- In 2014 35% of London jobs required canditated to be educated at a degree level.
- Resulted in more than a third of graduated from all UK universities migrating to London in their 20s.

Jamaica's Structural Adjustment Programme
- Joined the WTO and got access to free trade.
Impacts
- Local farmers complaining foreign food destoryed chance of selling local food.
- Free trade made Jamaica poorer and depend on foreign imports.
- Jamaicas debt is rising to $7 billion.
- Destoryed their dairy industry and other local industries.
- Government spends twice as much on debt repayments than it does on education and healthcare.
- IMF had to give Jamaica a $1 billion loan.
- 1990 97% of children went to school now only 73% attend..
- 1990 59/100,000 mothers died in childbirth, now increased to 110.

IGO- CITES
CITES = Covention of International Trade in Endangered Species.
Who?
- International Agreement
What?
- Ensures that internationla trade of animals and plants dont threatern their survival.
- Protects 35,000 flora and fauna.
Successful?
- Not very.
- Enforcement has not been strict enough.
Trade Blocs- NAFTA
NAFTA = North American Free Trade Agreement
What?
- An agreement signed by USA, Canada and Mexico.
- The agreement came into force on 1st January 1994.
- Created free trade in North America.
IGO - UNCLOS
UNCLOS = UN Convention on the Law of the Sea
When = 1994
Who = International Agreement
What?
- Defines rights and responsibilities to nations in using the oceans.
- Provides guidlines for managing marine resources.
- Creates exlusive economic zones and the owning country have sole exploitation rights over resources.
Successful?
- Yes
- Has 157 memebers .
IGO- Water Convention, Helsinki
What?
- Aims to protect the quantity, quality and sustainable use of transboundry water.
Successful?
- By 2012 45 nations had signed up.
IGO- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment
When = 2001
What?
- Assess consequences of ecosystem change and actions needed to conserve and use ecosystems sustainability by appraising them and the services they provide.
IGO- Antarctic Treaty System
Before
- Discovered 1820.
- No natives or government.
- 1950s lots of countries tried to claim it.
Artic Treaty
- De-militriased zone and nuclear free zone.
- Information about Artic is freely exchanged.
- Territorial claims suspended.
- Any UN member can sign up.
- Every country needs a scientific base there.
- No drilling or mining till 2048.
Threats to the Treaty
- Tourist numbers are increasing.
- Climate change
- Mineral expoloitation
Mini Car Company
- A foreign owned company based in the UK.
Owner = BMW (Germany)
UK Location = Oxford
- Seen to be a very Britsh car company using the union jack as decoration on the cars.

Russian Property in London
Russians
- 2013 Russians were top of the list of foreign buyers of London homes.
- Londons famous Belgrave Square has been occupied by so many Russian owners that it has been nicknamed the Red Square as 27/30 properties are owned by foreign nationals.
Non-national Investors
- Non-national investors have bought some of the most recognisbale locations such as the Shard or Canary Wharf.
- 2008-2015 over £100 billion worth of property in London was bought by foreign companies.

Strong National Identity- Catalonia
Facts
- Catalonia is Spains wealthiest region as it produces 20% of its wealth.
- It would be the worlds 34th largest economy if it became independent.
- Has high levels of self-government with responsibility for healthcare, education, police etc.
Reasons for Wanting Independence
- Many Catalans believe in a Spain with distinctive regions, languages and cultures.
- Catalonian people indentify themselves as Catalans not Spanish.
- They feels they contribute more than their fair share of taxes to the nation and they they subsidise poorer nations.
- 2010 half od Catalonians wanted independence.
- 2012- 1.5 millon Catalans demonstrated, demanding an independence referendum.
- 2014- A mock referendum was held, 80% wanted seperation from Spain.
- 2015- Pro-independence parties won a majority in regional elections.
- 2016- Catalan regional government drew up a strategy to hold a full referendum about independence but Madrid blocked it.
Failed State
Examples
- Somalia
- Yemen
- Libya
- Zimbabwe
How have they failed?
- Political or econimic system has become so weak that the national government is no longer i control and cannot maintain law and order.
- There is low life expectancy, undemocratic goverment, social unrest, poverty...

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Edexcel A-Level Geography Paper 2 | [6th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- OCR A Level Geography Human interactions H481/02 - 8 Jun 2022 [Exam Chat] »
- OCR A-Level Geography Human Interactions | [6th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- 2024 predictions »
- AQA A Level Geography Paper 2 7037/2 - 8 Jun 2022 [Exam Chat] »
- Geography A-Level »
- Who regrets the outcome of Brexit?? »
- -- »
- Need help to find references »
- Grow your Grades blog 23/24! »

Comments
No comments have yet been made