Two scientists, James Watson and Francis Crick, worked out the structure of DNA. By using data from other scientists they were able to build a model of DNA.
The data they used showed that bases occurred in pairs. Further x-ray data showed that there were two chains wound into a double helix.
A double helix
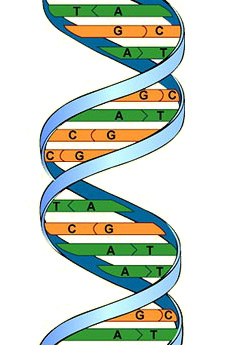
Base pairs on a DNA molecule
Each strand of DNA is made of chemicals called bases. Do not confuse these with the bases you meet when you study acids and alkalis in chemistry. There are four different types of bases, shown as A, T, C and G in the diagram.
In DNA, two strands coil together to form a double helix. There are chemical cross-links between the two strands, formed by pairs of bases.
Comments
No comments have yet been made