Genes and Health
- Created by: CookieMonster121
- Created on: 30-05-18 20:18
Alveolar properties for diffusion?
- Large surface area to volume ratio - alveoli are small and there are many of them - surface area of lung 70m2 - surface area to volume ratio directly proportional to rate of diffusion
- Concentration gradient - diiffusion rate directly proportional to the difference in concentration across the gas exchange surface - breathing + constant supply of blood maintains an efficient concentration gradient
- Thickness of gas exchange surface - inversely proportional to the rate of diffusion - alveolar and capillary cell membranes only one cell thick reducing diffusion distance
- Moistness of cell surface - lowers surface tension allowing gases to dissolve + surfactant means that the alveoli do not collapse
Fick's Law of Diffusion
![]()
- Epithelial cells - line cavities and the surfaces of internal organs
- Squamous epithelium - in alveoli and capillaries - secrete surfactant
- Globlet cells and glandular tissue - columnar epithelium - ciliate tissue lines trachea and secretes and moves mucus
cell membrane structures and functions
Phospholipid bilayer (polar hydrophilic head, nonpolar hydrophobic tails) - semipermeable barrier which only allows water and gases easily through, large or polar molecules can only cross the bilayer with the assistance of other structures, fluidity allows movement of structures within the bilayer
Glycoprotein (carb attached to protein) and glycolipids (carb attached to phosphlipid) cell signalling and recognititon
Cholesterol - membrane and stability and fluidiity - makes barrier more complete
Integral proteins - channel proteins and carrier proteins - allow movement large, polar molecules through the phospholipid bilayer
Cell membrane models
1. Dawson-Danielli Model - three layers two dark outer layers (proteins) and a light inner region (lipids) - evidence from electron micrographs - doesn't allow for hydrophilic phosphate heads to be in contact with water, nor any nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids on the outside of membrane proteins to be kept away from water
- But phosphate heads are more electron dense and show up as darker edges to the membrane, with lipid tails the lighter inner part
2. Singer-Nicholson/ Fluid Mosaic Model
- Two types of proteins on membranes - peripheral and integral proteins, integral proteins had polar hydrophilic amino acids at their ends, and nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids in middle
- Freeze-fracture microscopy studies - frozen membrane sections were fractured along the weak point between the lipid layers and the inner fractured surface coated with heavy metal - scanning electron microscopy revealed a smooth mosaic-like surface interspersed with much larger particles
- Fluidity - fluorescent antibody tagging of membrane proteins - green and red markers on different cells proteins - the markers become intermixed when the cells fuse
Describe types of active transport
Active Transport - movement of substances against the concentration gradient which requires expediture of energy in the form of ATP - ADP + Pi
Carrier Proteins - ATP used to change the shape of the carrier protein allowing a molecule to cross the membrane
Exocytosis - used for bulk transport out of the cell - vesicles fuses woth the cell membrane releasing their content
Endocytosis - bulk transport into the cell - vesicles are created on the cell surface membrane, brining their contents into the cell
Describe types of passive transport
Passive Transport - movement of substances across a membrane with out an imput of cellular energy
Diffusion - unassissted met movement of molecules from an area of hig concentration to an area of low concentration down a concentration gradient until an equilibrium is reached
- hydrophobic (lipid-soluble) or small uncharged ions through the phospholipid bilayer
Facilitated diffusion - transport of a substance down a concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area of lowe concentration until an equilibrium is reached
- hydrophilic molecules or ions through channel proteins or carrier proteins
- Channel proteins - specific shape that permits the passage of one type of ion or molecule
- Gated channels - can be open or closed depedin on the presense or absence of a signal e.g hormonal, change in potential difference
- Carrier proteins - molecules bind onto specific site on the protein causing the protein to change shape and the molecule crosses the membrane
Osmosis - a type of diffusion but of water molecules from a dilute area to a concentrated area through the phospholipid bilayer until both sides are isotonic (equally concentrated)
Structure of DNA
- Gene - sequence of bases on a DNA molecule that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids on a polypeptide chain
- Genome - all the genes in an individual or species
Nucleotide
- Organic bases - Adenine(A), Thymine (T) , Guanine (G) , Cytosine (C) - Complementary base pairs (A,T) and (G,C) - hydrophobic - 3000 million of these base pairs
- Phosphate group
- Dexoyribose (pentose sugar)
- Phosphate group + pentose sugar - backbone
- Glycosidic bond (base and sugar), ester bond (phosphate and sugar)
Polynucleotide
- Phosphodiester bond between two nucleotides, hydrogen bond between two bases
- Antiparallel - two nucleotide strands are antiparallel as the run in opposite directions 5' to 3' or 3' to 5'
Structure and types of RNA
DNA - double stranded polymer, antiparallel double helix, uses AGCT, pentose sugar- deoxyribose
RNA - single stranded polymer, uses AGCU (RNA never contains thymine, uracil energetically cheaper), ribose sugar
messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) - produced during transcription, carruers the code from the DNA to the cytoplasm
Involved in translation
- transfer RNA (tRNA) - each type of amino acid has its own type of tRNA, which binds to the amino acid and carries it to the growing end of the polypeptide chain
- ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Genetics definitions
- Genome - the complete set of genes in a cell/organism
- Proteome - The full range of proteins a cell can make
- Gene - sequence of bases that codes for a sequence of amino acids that makes a specific polypeptide chain
- Locus - position of a gene on the chromosome
- Haploid - contains one copy of each gene (23 in humans)
- Diploid - nuclei containing two copies of each gene (46)
- Allele - variation of a gene
- Genotype - The combination of alleles in an organism
- Phenotype - the physical expression of the genotype and its reaction with the environment
- Dominant allele - an allele which is always expressed
- Recessive allele - ony expressed when homozygous
- Codominant allele - both alleles are expressed/both are dominant
- Homozygous - both alleles are the same
- Heterozygous - the two alleles are not the same
Nature of the genetic code
- Non-overlapping - successive triplets are read in order, each triplet code is adjacent and seperate
- Degenerate - different codons can code for the same amino acid
- Universal - Each triplet code codes for the same amono acid in all living organisms
Codon - triplet code - triplet of bases on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid
Anticodon - triplet bases on tRNA that is complementary to codon on mRNA
Template strand (antisense strand) - DNA strand with bases complementary to those needed to make protein
Coding strand (sense strand) - same base sequence as that needed to make a protein
Protein synthesis
Transcription - process by which a complementary mRNA copy is made of the specific region of the DNA that codes for a polypeptide
- DNA Helicase - seperates the DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds
- Complementary base pairing by RNA polymerase, which catalyses the reaction - binding DNA to free RNA nucleotides
- An mRNA strand forms with phosphodiester bonds between the RNA nucleotides, mRNA, having broken off the DNA, exits the nucleus through nuclear pores in the nuclear envelope
- H-bonds reappear and the DNA zips itself back up
Translation - turning the specific sequence of bases in the genetic code into a sequence of amino acids
- Initiation - ribosomes (rRNA and proteins) assemblt around the mRNA forming a polysome, complementary anti-codon of tRNA-amino acid complex attracted to the start codon (AUG)
- Elongation - mRNA is read one codon at a time and an amino acid matching each codon is addied to a growing polypeptide chain - tRNA binds to codon, existing polypeptide chain is linked onto the amino acid (peptide bonds), mRNA is shifted one codon on. exposing a new codon for reading
- Termination - finished polypeptide chain is released, stop codon (UAA, UAG, UGA) read
Protein structure
Structure of an amino acid - an amine group, carboxylic group and a variable functional Residual (R) group - 20 differrent amino acids, uncharged or polar, amphoteric react as a base/acid
Formation of polypeptide - condensation reaction (removal of H2O) to form a dipeptide with a peptide bond - repeated to form a polypeptide chain of up to 1000 amino acids
- Primary structure - sequence of amino acids on the polypeptide chain
- Secondary structure - interactions between the amino acids in the polypeptide chain causes the polpeptide to twist and fold into a 3D shape
- a-helix - twisted to look like an extended string
- B-pleated sheets - fold back on themselves or several lengths of the chain may link together to form parallel chains
- Tertiary and quaternary structure - production of a more precise 3D shape - disulphide bridges, ionic bonds, hydrophilic polar R groups attracted to other polar molecules, hydrophobic nonpolar molecules inside protein
- Conjugated Protein - another chemical group associated with their polypeptide chains
Protein structure - globular and fibrous
Globular proteins e.g haemoglobin, enzymes, antibodies
- Polypeptide chain folded into a compact spherical shape
- Soluble due to hydrophilic side chains that project from the outside of molecules - important for metabolic reactions
- Three-dimensional shape crucial to their roles in binding to other substances
Fibrous proteins e.g keratin, collagen, tendons, bones, cartilage, blood vessel walls
- Remain as long chains
- Several polypeptide chains can be crosslinked for additional strength
- Insoluble proteins
- Important structural molecules
Enzymes
Enzymes - globular proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions, every reaction in the cell is catalysed by a specific enzyme
- Specific - precise 3D shape includes an active site - enzyme can only bind to one substrate
- Lock-and-key theory - substrate molecules form temporary bonds with the amino acids of the active site producing an enzyme-substrate complex - which catayses the reaction - products released leaving the enzyme unchanged
- Induced fit theory - only a specifically shaped substrate will induce the correct change in shape of an enzyme's active site, which enables the substrate to react
- Reduce activation energy - electrically charged groups on their surfaces interact - this attraction distorts the shape of the substrate and assist in the breaking/formation of bonds
- Intercellular reactions (inside cells e.g. metabolic pathways such as glycolysis), extracellular reactions (outside cells e.g. digestive enzymes)
- Anabolic reactions (building up) and catabolic (breaking down)
DNA Replication
Process - semi-conservative replication
- Unwinding of the helix structure - DNA helicase - seperates DNA double helix into single strands as the hydrogen bonds break
- Free DNA nucleotides line up alongside each DNA strand and hydrogen bonds form between the complementary bases, DNA polymerase links adjacent nucleotides with a phosphodiester bond in condensation reactions to form new complementary strands
- Tow indential daughter strands are created
- Leading strand (5' to 3' direction)- synthesised continuously, DNA polmerase adds nucleotides to the deoxyribose 3'ended strand
- Lagging strand (3' to 5' direction) - synthesised in fragments - nucleotides cannot be added to the phosphate 5' end as DNA polymerase can only add DNA nucleotides in a 5' to 3' direction, and fragments are then sealed with ligase
Different models of DNA replication
Conservative model - one DNA molecule has two origional parent strands, the other molecule has two 'new' strands
Fragmentary replication - all DNA strands are made up of a mixture of origional parent DNA nucleotides and new nucleotides
Semi-conservative replication - each DNA molecules contains one origional parent strand and one new strand
Meselson and Stahl Experiment
- Grow E.Coli in a medium containing N15 - a heavy isotope of nitrogen, bacteria take up nitrogen to make new DNA - after many generations all DNA labeled with heavy N15
- Switched to a medium containing N14 - a light isotope of nitrogen an allowed to grow for several generations - DNA made after the switch would contain N14
- Density gradient centrifugation - Able to extract and purify DNA of each generation of E.coli - measure the density of the DNA - spinning them at high speeds to seperate the DNA into bands in the presence of caesium chloride - allowing small differences in density to be detected
Mutations
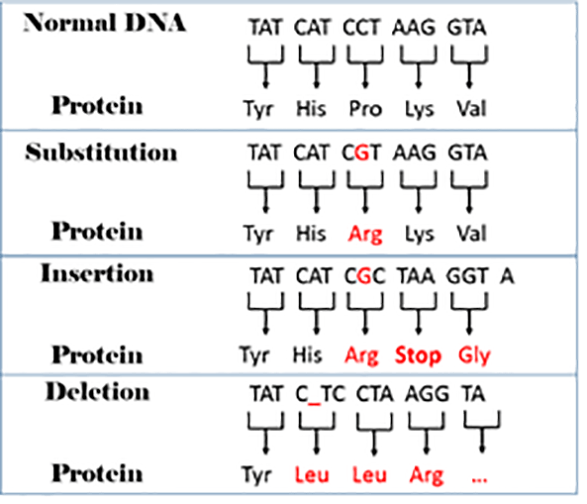
Sickle cell anaemia - substitution mutation in the gene that codes for polypeptide chains in the haemoglobin --> GUA rather than GAA -- half moon (sickle) shaped cells that carry less oxygen and can block blood vessels
CF gene - hundreds of different mutations can give rise to cystic fibrosis - most common is the DF508 mutation, the deletion of three nucleotides causing the loss of phenylaline - misfolding of the CFTR protein
Patterns of Inheritance and disease
Monohybrid inheritance - characteristic is controlled by only one gene
Recessive alleles often have a heterozygous advantage
Cystic Fibrosis
- 1 in 25 are cystic fibrosis carriers (Ff) - can pass the gene onto their children
- Every time a child is born to parents who are both carriers of cystic fibrosis there is a 1 in 4 chance that he will have the genotype (ff) and have cystic fibrosis, 1 in 4 that the genotype will be (FF), 2 in 4 that they will be a carrier (Ff) - punnet square
- Ff - some protection against typhoid
Albinism, phenylketonuria, thalassaemia (have protection agaisnt malaria)
Dominant alleles e.g. Huntington's Disease
Punnet squares and Genetic pedigree diagrams
Regulation of mucus water content in lungs
Excess water in the lungs
- Presence of excess water is detected by the epithelial cell membranes
- Carrier proteins in the basal membrane of the epithelial cells actively pump bacteria out of the cells
- The concentration of sodium inside the cell falls, setting up a concentration gradient across the apical membrane - sodium ions diffuse from the mucus down this concentration gradient into the epithelial cell by facilitated diffusion through sodium ion channels
- Raised concentration of NA+ in the tissue fluid creates a potential difference between the mucus and the tissue fluid which causes Cl- to diffuse out of the mucus into the tissue fluid via the gaps between neighbouring epithelial cells
- Overall effect to increase concentration of Na+ and Cl- in the tissue fluid - water is drawn due to osmosis into the tissue fluid through the basal membrane - increasing the overall solute concentration within the cell
- Water is drawn out of the mucus via osmosis over the apical membrane
Regulation of mucus water content in lungs
Too little water in the lungs
- Cl- ions transported across the basal membrane into the epithelial cell
- Creating a concentration gradient across the apical membrane (more Cl- in the cell than in the mucus)
- This causes the CFTR protein channels to open (type of gate channel protein)
- Choride ions diffuse out of the cell via the CFTR channels, which, when open blocks the NA+ channels
- Build up of negatively charged chloride ions in the mucus creates an electrical gradient between the mucus and the tissue fluid
- Sodium ions diffuse along this gradient from the tissue fluid to the mucus
- Causes the movement of water into the mucus intil the solutions are two viscous
CF lung
- CFTR channel ins absent or nonfunctional
- The sodium channels are therefore always open and hence there is continual water reabsorption from the mucus into the epithelial cells
- The raised level of sodium in the cells and tissue fluid then draws chloride ions out of the mucus
- Making the mucus even more viscous
Difficult for beating cilia to move the mucus
Mucus is not effectively cleared out of the lung - reduces the effectiveness of the alveoli
Mucus frequently becomes infected with alveoli - phagocytic cells over-produced in response and when they break down, their DNA makes the mucus even more sticky - downward spiral of airway inflammation and lung damage
Effect of cystic fibrosis on other body systems
Digestive system
- Cystic fibrosis sufferers have to eat 120%-140% of the recommended daily intake and may take digestive enzyme supplements
- The pancreatic duct becomes blocked by sticky mucus, impairing the release of digestive enzymes
- Lower concentration of enzymes in the small intestine reduces the rate of digestion - food is not fully digested so not all nutrients can be absorbed - malabsorption syndrome
- Pancreatic enzymes can become trapped in the pancreas which can damage the pancreas - the development of a hard cyst of damaged or fibrosed tissue
- If damage occurs within the cells that produce insulin a form of diabetes can occur
Reproductive system - infertility
- Mucus plug develops in cervix (female)
- Lack of vas deferens (male) - sperm cannot leave the testes, or the vas deferens is partially blocked
Sweat - hypotonic sweat with excess salt
Genetic screening - types
Genetic testing - identifying the abnormal allele of the gene in the DNA of any cells, Genetic screening - to confirm a diagnosis ( currently impossible to test for all of the hundreds of possible mutations that lead to CF), to identify carriers - to enable parents to make informed decisions about how to proceed
Genetic screening to test embryos
- Amniocentesis - insertion of a needle into the amniotic fluid to collect fetal cells that have fallen of the placenta and fetus - 15-17 weeks of pregnancy
- Chronic villus sampling (CVS) - small sample of placental tissue is removed either through the wall of the abdomen or through the vagina - 8-12 weeks of pregnancy
Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) - when an early embryo is growing in a culture and has arround 8 cells, one cell can be removed without damaging the embryo - the DNA of the cell is them analysed
- Risk of miscarriage to potentially healthy fetuses
- Abortion - less difficult physically and emotionally earlier on
- IVF - lower chance of success
Ethical Framework
1. Rights and Duties - e.g. human rights, duties to others - religious faith, social conventions built up over thousands of years
2. Utilitarianism - maximising the amount of good in the world - no moral absolutes
3. Making decisions for yourself - informed consent and autonomy -
- A utilitarian would say that autonomy is only desirable if overall benefits are greater than the overall costs
- Someone who believes in rights and duties might argue that each of us has a right to autonomy but also has a duty to take into account the effects of our actions on others
- Not everyone can give consent; learning difficulties, dementia, too young; advocate may be appointed
4. Leading a virtuous life - a good life consists of acting virtuously - traditional seven virtues - justice. prudence, temperance, fortitude, faith, hope and charity - different people might have different opinions on what is virtuous
Related discussions on The Student Room
- GCSE English Language Speech Opinions »
- Biology Paper 2 AQA Triple Higher 2023 »
- PCR A level biology »
- 25 mark essay question »
- 25 marker essay biology »
- AQA A-Level Biology Paper 2 [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Eduqas A-Level Biology Component 2 [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
- Advanced Higher Biology Project Ideas »
- Meiosis help alevel »
- OCR A A-Level Biology Biological Diversity [16th June 2023] Exam Chat »
Comments
No comments have yet been made