Introduction to Economics Sept 2017
- Economics
- Factors of production Economic agents Markets The demand curving- left, right, extension, contraction. Factors that affect the demand curve PASIFIC Types of goods
- GCSE
- AQA
- Created by: AlexK03
- Created on: 13-02-18 08:20
Factors of production
Resources- to make our wants and needs but are limited, i.e. fossil fuels & oil, (scarce)
Labour- Human input in production process ( not all human capital have the same skills, experience & education )
Lands-includes actual land and the resources surrounding it I.E; Sea, rivers, oil.
Capital- Goods that are used to produce other goods and services, I.E; factories machinary. this is MAN MADE ONLY!
Enterprise- people who take risks are known as entrepreneurs & take risk by creating things from the other three factors of production. I.E. if business fails then money is lost but if business is successsful then the reward is profit
- Basic example of each factor;
Labour- Fast food worker, Bin men/women, teacher etc etc.
Land- Wood, cotton, wood etc.
Capital- Washing machine, pencil case, table etc.
Enterprise- Business man/ woman, Restaurant manager etc.
Economic agents
The three econmic agents in the economy are; Producers, goverments, consumers.
Producers:
- Firms or people that make goods or may provide services
- Decide how much to make & to sell it for
- Need to think about what to produce, and what is most cost effective wya to increase the profit margins
- Business failure would be blockbusters as they didn't listen to customers to go online and Netflix overtook their customers.
Consumers
- People or firms that buy goods and services
- Can be a firm which needs to buy products to make final product i.e. machines or ingrediants
- Decide what they want to buy and at what price, as they are buying the product
Goverments
- Sets rules that the customers and producers have to follow
- Have to decide how much to get involved
- I.E. laws that make sure the producer is advertising the correct weight and ingrediants on food.
Markets 1
Markets- where buyers & sellers come together and exchange goods and services- doesn't mean face to face.
Planned economy:
- How the goveremnt allocates resources
- Not market & this is rare
- North Korea is an example of planned economy
Free market/ market economy
- Allocate resources based on supply and price mechanism
- Private mechanism- will sell for any price anyone is willing to pay
- By private individuals and firms
Mixed Economy
- Combine free market and goverment intervention
- Privately owned business makes up the private sector, whereas the goveremnt is public sector
- Work together to allocate resources, and the goverment has intervention/ biggest say
- Mixed economy has public and private sectors
Markets 2
Advanatges of free market;
- Tax not having to be paid
- people have more disposable income to spend on businesses
- producers don't have to spend lots of money of safety regulations
- no restirctions
disadvantage of free market;
- competition between compnaies will occur
- workers aren't paid minimum wage, struggle to buy essential items ( needs )
- possibility of dangerous chemicals, (carcinogenic items)
- workers in dangerous conditions
Entrepreneurship- reward for good ideas and encourages risk taking
Choice- risk taking leads to better choice so the consumer has no restrictions
The demand curve
Demand- is the amount of a product that comsumers and customers are willing to pay and are able to buy at that specific point in time.
If the demand curve moves to the right = increase and left = decreae
- As the price increase the quantity demand then decreases, but if the price decreases the quantity demand increase, inverse relationship
Contraction- Demand decreases due to price increase Extension- demand increase due to price decrease
PASIFIC
- Population- the amount of people present if a country ( if the business isn't E-commerce ) will affect if the business will stay alive due to the profit
- Advertisment- The increase in advertisement will create awarness which will inturn cause the demand curve to shift to move outwards ( right )
- Substitute-price- Not the same product but the same end product
- Income- The average income falling ( recession i.e. Uk 2008 ), will affect demand and make normal goods fall, and inferior good dmeand increase
- Fashion and trends- tastes are constantly changing, I.e. Beauty and clothing stores, so for them to stay alive they needs rapid changing stock, for example: seasonal clothing.
- Interest rates- Borrowing goes up and items that require a loan means that the demandwill go up
- Compliments- a 'good' bought along side another 'good' for example fish and chips.
This is a acronym for PASIFIC, which causes a shift in the demand curve
Types of goods
Normal goods:
- If prices increase then demand will decrease
- if prices decreases then demand will then increase
- Most goods and services are then classes as normal goods
Consumer income:
- General rule- as income increases demand increase vice versa
- Most disposable income lead to increase spending
- Luxary goods- are likely to have demand fall quicker if income falls
- Necessity items- will see little to no change in income falls, but inferior shops like Aldi & Lidl will see a larger demand
Normal goods= Heinz, Walkers crisps
inferior= ASDA smart price stock.
Contraction and Extension diagram & info
TO GET FULL MARKS YOU MUST LABEL AND PUT THE CORRECT ARROW:
- UP FOR CONTRACTION
- DOWN FOR EXTENSION
- AND IF THE DEMAND CURVE IS EITHER CONTRACTION/ EXTENSION DRAW ONLY ONE DEMAND CURVE LINE AND ON ARROW.
Left shift & Right shift Diagram and Info
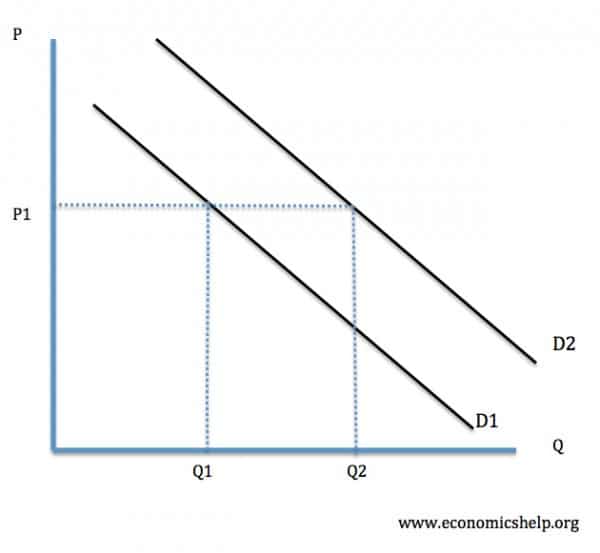
You must label the graph and each deamnd curve line with D1 or D2 depending on whether it's right or left shift
D1 = the original demand curve
D2= the current demand curve
in the diagram above this is right shift as the outer line = right shift and the inner line = left shift
Related discussions on The Student Room
- economics essay »
- If you done/doing a degree, what are the best books you recommend for your subject(s) »
- AQA 25 marker structure »
- History »
- nea geography »
- how do you answer a 9 marker in geography »
- gcse history qa paper 1 exam »
- Supply and Demand for Oil »
- a level history - edexcel cold war coursework »
- Personal statement HELP - econ »
Comments
No comments have yet been made