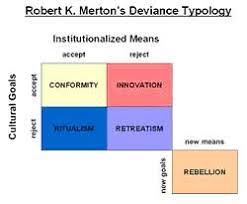
1. CONFORMITY: Strive towards goals legitimately.
2. INNOVATION: Have the goal of money success but strive to it illegitimately.
3. RITUALISM: Give up on goals, but still live a legitimate life and follow rules for own sake.
4. RETREATISM: Reject goals and legitimate means, becoming drop outs e.g. tramps.
5. REBELLION: Reject societies goals and legitimate means replacing them with new ones as they desire a revolution e.g. politicians.
Comments
No comments have yet been made