Case Studies
- Geography
- Population DynamicsConsuming ResourcesGlobalisationDevelopment DilemmasThe Changing Economy of the UKThe Challenges of an Urban World
- GCSE
- Edexcel
- Created by: EA12570
- Created on: 25-02-17 20:14
Tar Sand in Canada
Benefits
- Largest oil reserve after Saudi Arabia with 300 billion barrels of oil extracted from the tar sand
- Produces huge profits for oil companies and tax benefits for countries with tar sand
- Means Canada will no longer have to be dependent on middle eastern countries for oil supply
- Extracting more oil will mean oil production will increase which means money will no longer need to be spent on switching to other fuels such as hydrogen
Costs
- Tar sand oil produce upto three times more greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide which contributes to global warming and climate change
- It is a more expensive form of oil so will be very expensive for the public
- Uses a huge amount of water - roughly six barrels of water for each barrel of oil and often the waste polluted water from extracting the tar sand is returned to rivers/lakes which contaminates water supplies.If contaminated water reaches water supplies, it could increase the risk of cancer for the locals
- Forest area will need to be removed which leads to massive scale deforestation
Wind Farms
Benefits
- Renewable energy source meaning it will never run out - infinite. This means we will no longer have to rely on fossil fuels which are running out as alternative methods like this can be used
- Creates little or no polluting gases therfore slowing down global warming and climate change
- Cheaper for people to use compared to non-renewable sources such as tar sand in Canada as wind is free
- Today, new wind turbines are being developed which are much more efficient
Costs
- Amount of of electricity generated is dependant on the strength of the wind and if there is no wind or hardly any no electricity can be generated.
- Productive costs are expensive and huge amounts of wind turbines are required to geenrate significant amounts of energy
- NIMBY's are huge opposition to wind farms as they find them ugly and noisy and do not want them in their back yard
- Electricity bills are higher
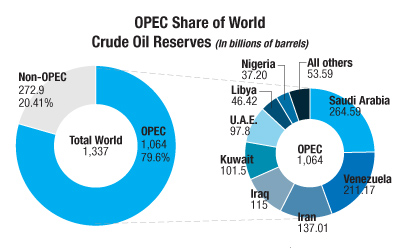
OPEC
- Try to preserve oil reserves for longer than those not within OPEC
- Works in determining production ans prices of oil
- Countries involved include :
- Saudi Arabia
- Kuwait
- Iraq
- Iran
- Controls the price of oil by slowing down production of oil as if there is less oil countries will compete to get what they need which will increase oil prices
Thomas Malthus
Theory
- Malthus is pessimistic meaning he believes only the worst will happen in a situation
- He believes that as a result of population increasing exponentially and food production increasing at an artithmetical rate, the population at one point will increase too much for food production to cope with.
- This will result in famine and war which will keep the population in check due to increase in mortality and population will later stabilise again until the next 'natural check'
Evidence
- His theory can be backed up with the following evidence
- Population is growing rapidly today
- There is a high demand for resources such as oil which are running out
- War, famine and disease do stop population growth
Arguments Against
- Improvements in technology and farming methods ie. fertilisers
- Increased production of food and resources to support developed countries
Esther Boserup
Theory
- Boserup is optimistic as she believes we will make the best of a bad situation
- She believes that whenever population puts a strain on resoruces new technologies and farming methods will be invented which as a result will increase food production
- She believes population will never outstrip food supply as even with all the problems in the world such as famine and war humans have always found a way to get over their problems and countinue advancing
Evidence
- Tractors - allows farmers to harvest and grow crops quicker
- Fertililser - allows crops to grow bigger, healthier and quicker which helps increase food production
- Crop-dusting - allowed large scale fertilising of crops
- Renewable energy such as wind power - means we are not having to use more fossil fuels which means that there is less pressure on non-renewable so they can last longer
- Advances in medicine such as new vaccinations - helps protect the population and keeps it thriving
UK Energy Policy
UK Government Energy Policy
- Supporting international action on climate change e.g. through UN agreements
- Increasing the use of low carbon technologies such as encouraging households to install solar panels
- Help households to out their energy bills by installing insulation or giving cash to households to encourage them to replace their boilers for new energy efficient boilers
- Regulating and licensing UK energy industries and infrastructure by taxing companies that produce too many greenhouse gases
Local Government Policy to reduce resource consumption
- Recycling helps with reducing resource consumption as it encourages people to reuse materials instead of throwing it away which puts less pressure on making more resources
- Cycle lanes reduces resource consumption as it encourages people to use bikes more often which does not run on oil or fuel
- Promoting farmers markets as it means that goods can be brought locally and therefore will not need to be purchased from elsewhere and will save fuel
- Bus lanes help as it encourages people to take public transport as it is faster
Ghana - Pre-Industrial Economy
Employment
- 50% of employed people work in the primary sector where people are working in farms which shows people still rely on agriculture. Some are even subsistence farmers. Many people work in the primary sector due to lack of skilled people
- Secondary sector is small (16%) and mostly filled up by men and many people work in the informal sector
Working conditions
- Working conditions are tough particularly in farms due to hard manual labour due to lack of mechanisation. Many people in the informal sector - mostly women and children likely to suffer abuse and exploitation
Ghana's export
- Ghana does not earn much from their exports of cocoa, diamonds and timber as these are raw materials and not the more expensive finshed manufactured products
- Future Sector - increase in tertiary jobs (which is at 33%) specifically in the tourist sector
China - Industrial Economy
Employment
- Two sectors that are growing rapidly are primary (48%)however secondary sector is rapidly growing
- The main reason for the primary and secondary sector to grow so quickly is due to China having a lot of energy supplies and a huge workforce
Working Conditions
- There is a lot of pressure- caused young workers to commit suicide due to the workload
- There are no safety laws which protects the workers and people are having to work long hours with minimal breaks and low wagesThe main reason why working conditions in China are poor is due to the fact there are no trade unions to support worker's rights. For instance there has been allegations of child labour in the past
China's Exports
- China's biggest exports include coal, natural gas, iron ore and manufactured goods which China earns a lot of money from
UK - Post Industrial
Employment
- Two sectors which have grown the most rapidly is the tertiary and quaternary sector which has increased due to the decline of the primary and secondary sector (under 20% in total)
- Primary sector has declined because technology has taken over work in this sector. Secondary industry has declined due to deindustrialisation as factories have closed down or outsourced to developing countries due to cheaper labour abroad
- The main group of people that this decline has affected is the factory workers as they have lost their jobs and may not be able to find a better job due to skill shortages
Working Conditions
- Have strict health and safety laws put in place which supports workers and have equal wages and have trade unions to support workers and laws to protect workers
UK's Exports
- Aircraft technology, finance and banking, electronics like Dyson which are worth alot
UN/WTO/IMF/World Bank
UN-Government from different countries coming together by making agreements that make the world a safer, healthier place with greater oppurtunities and justice for all
WTO-It deals with the rules of trade between countries to ensure that trade flows as freely as possible by dealing with any disputes between countries who have previously made trade agreements and ensure that businesses conduct their business without exploitation
IMF-It is an organisation (188 memeber) working together by keeping track of the global economy and the member countries by lending to countries with payment difficulties and giving practical help to members
World Bank-Is a source of financial assistance which provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes in attempts to reduce poverty
Containerisation
How has International trade grown so rapidly?
- Shipping
- This has increased global trade because as ships have gotten bigger, larger capacity of goods can be transported at once
- Containerisation
- This has increased global trade as it makes it easier to load and ship goods quickly and more efficiently. It is also cheaper because more can be transported in one go
- Aircraft
- This has increased global trade as it is a faster method to get around and has allowed more important goods such as medical equipment to be transported quickly during an emergency. Only 2% of our goods are transported by air which makes up 15% by value
Nike
- TNC in secondary sector
- Headquarters in Oregan where product design is carried out
- Nike has outsourced production to South Korea and Vietnam as it is cheaper to make goods there due to cheap labour abroad
- Nike's research and development team is kept in the USA due to better educated teams present in USA and more money can be spent on research
- Most Asian countries get the less profitable, production activities
BT
- BT is a British-owned telecommunications company which deals with telephone rentals, broadband, mobile phones, industrial communications for factories e.t.c
- Host country is UK
- Operates in 170 countries
- Areas of the business such as services like call centres, software developments and company accounting are done overseas in places like Bangalore and New Delhi due high skilled IT graduates
- BT operates in developed countries such as Russia, USA which shows it is an example of a footloose company as it can locate anywhere as long as it has access to high quality communication links
- Has offices in India due to its reduced taxes and skilled technology graduates
- Call centres in India has resulted in issues in developed countries as by outsourcing business abroad many people have lost their jobs in call centres
Malawi - Barriers to Development
- Landlocked Country
- Has no coastline-no ports which to export or import goods from
- Has to pay neighbouring country - Mozambique who have a singe tracked railways which is slow and very expensive for Malawi and delays arrival of vital supplies
- This makes goods from Malawi expensive and uncompetitive so other countries do not buy from them
- Trade
- Most of Malawi's exports are raw materials such as wood which aren't worth a lot of money
- EU and US place tariffs on finished goods such as roasted coffee beans which means that they are not earning much profit from trade as companies would rather buy the raw material. This has also stopped them from developing their industry
- HIV/AIDS
- Most people affected by HIV/AIDS in Malawi are economically active (20+) leading to low life expectancy. This makes people too weak to work so they don't pay taxes
- Treatment is expensive and therefore many families cannnot afford it
- Could push family into poverty if wage earner of family gets this virus
- Lots of orphanes so can't get jobs
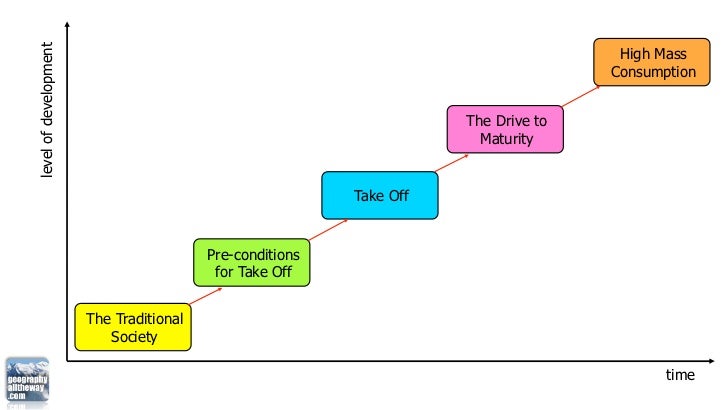
Rowstow's Modernisation Theory
- This graph shows how countries develop over time by going through different stages of development as income rises
- First stage - The Traditional Society i.e. Malawi where most people work in agriculture.
- Malawi may eventually earn enough money and improve its infrastructure enough to build secondary industries and move to the third stage which is the take-off stage
- Take-off stage will allow incomes to increase and eventually people will be able to afford more consumer goods and reach the high mass consumption stage where the UK is today
- Take-off stage will allow incomes to increase and eventually people will be able to afford more consumer goods and reach the high mass consumption stage where the UK is today
Frank's Dependency Theory
- Is based around the idea that developed rich countries (core) are limiting the level of development of the poorer countries (periphery) from the control of the world economy.
- The most developed countries are able to exploit less developed countries through the use of their economic and political power. The Dependency theory also suggests that the unequal pattern of development has been reinforced by:
- Rich countries imposing trade barriers and conditions for loans. E.g. Malawi has to trade unroasted coffee beans which are not worth much as USA and the EU put tariffs on finished goods.
- Unbalanced trade - Resources are being sold by the periphery and are not worth much money. The core then sell manufactured goods back at a higher cost which keeps the periphery poorer and the core richer
Bihar & Maharashtra (India)
Bihar (Rural Periphery)
- It is India's poorest state with 86% of its population is rural
- Annual Income is low - 6000 rupees (£75) per person- 33% of India's average income
- Half of Bihar's household live below poverty line and 80% work in low skilled job
- Only 59% of Bihar's population has electricity
- The main type of farming in Bihar is subsistence farming. In addition lots of young people are leaving Bihar to work in core region of India - leaving Bihar in even worse situation
Maharashtra (Urban Core)
- Mumbia, the main large, famous city is located here
- Maharashtra has experienced such growth and has become a core region because of:
- Services - Graduates from Mumbia's Uni often find jobs with large TNC's (e.g.BT)
- Manufacturing - Industries such as clothing, food processing, steel and engineering
- Entertainment - Mumbai has the world's largest film industry (Bollywood)
- Construction Boom - Increased population as attracts economically active people however due to larger scale migration, people are unable to find work -slums
Katse Dam, Lesotho
South Africa
- Provides clean water for lots of people including Johannesburg and people living in the poorer townships who now have access to clean water which is main purpose of the dam
- The dam can be used by Industries in many ways such as to generate electricity
- Costs a lot of money to build aswell as maintain leading Johannesburg to borrow huge sums of money from the World Bank
Lesotho
- Lesotho can earn a lot of money by selling the water to Johannesburg
- Has provided 7,000 jobs and reduced unemployment
- Many people have been forced to leave their homes because the land has been flooded to make space for the reservoir
- Subsistence farmers have been forced out of their lands and therfore farmers have lost money
- Local people have to travel further just to get basic amenities like clean water
- Natural ecosystems destroyed and habitats disrupted due to flooding of large areas
Small Wells, Tanzania
- WaterAid supplys technology, information and advice by working with local NGO's who the villagers liaise with
- Through commitees the local village decides where the well will go and organise the work
- The well is built by the villagers using appropriate technology that they are able to maintain and some villagers are giving training to look after the well and carry out any repairs in the future
How it helps the villagers
- Now have access to clean water which wasn't accessable before which means less time wasted on fetching water and fewer sick people unable to work
- With this clean water, crops can be grown which can later be sold for a profit
- This increased income in the family that people can then afford to send children to school
- These children gain qualifications and get better jobs which can improve the economy of Tanzania
M4 Corridor
- Runs from West of London to Cardiff in Wales
- Reasons why it attracts the Knowledge Economy:
- Good education and universities i.e. Oxford for enterprise & research
- Close to heathrow which is one of London's main airports which shows good transport links
- Close to Hi-tech firms and research centres
- Industries are close to M4
- Lots of workers in area
Dinnington, South Yorkshire
Changing Employment (Secondary- Tertairy)
- Past Employment
- Most jobs were done by men in mining i.e. Coalfield Colleries which were later closed down by the government in 1922
- Current Employment
- Most people now have to work in retail
- Most work is found futher away
- Most companies there are in tertiary sector such as home delivery or sales
- Most working in nearby Business Parks which created 1,700 jobs
- Problems with changes
- People have to commute instead of working locally
- Only some jobs were permanent but many were temporary or contract posts for a few months only
- Many jobs gave low wages
- Some seasonable retail jobs
The NE & The SE
North East (Newcastle, Durham, Middlesborough)
- Lowest income region with average household income of £26,000 per year - UK's 12th Standard Economic region
- Most deprived region with high unemployment (11% -2012) and poor health as has worst indicator in England for deaths by smoking and early deaths from heart disease
- In 2011, 1/4 of all jobs were in public sector. Public sector jobs were reduced due to reduced government funding - 32,000 jobs lost
- 'Domino effect' has affected NE as all of NE's major industries such as coal, steel, engineering and shipbuilding have all suffered from globablisation and therefore closed down or moved businesses abroad. For example shipbuilding and engineering industry collapsed when Asain countries began to build larger ships and due to cheaper labour abroad.
- Current situation : Manufacturing has declined and tertiary sector has increased. Private companies have also located there such as The Sage Group - 1st major software business to locate there
Glasgow
Secondary Industry in Glasgow
- Glasgow once had a ship building factory however overseas competition caused decline
- This also caused a decline in steel making and coal mining (Domino Effect)
- Positive Impacts Reduced noice and air pollution
- More land available for development
- Prevents traffic congestion near factory as not many workers now have to go to work
- Negative Impacts
- Loss of income for workers which leads to migration as skilled workers move to find jobs
- Derelict land looks unsightly and deteriorates infrastructure which increases vandalism in area which government have to pay a lot to clean up
- Manufacturing further away leads to increased transport and air pollution
- Glasgow have diversified as tertiary and quaternary industries have expanded in areas such as media and science centres have been opened
Fort Dunlop
- Located in NE of Birmingham at M6 directly near the city centre
- Tyre Production
- Used to manufacture tyres by September 2014
- Large-scale tyre production employed over 12,000 people
- It is now a multiple- use complex, with offices, retail and a Travelodge
- Good example of Brownfield development as
- Exellent transport links as close to motorway
- Turned a derelict building into a multiple-use complex
- Provided several jobs
Newcastle Great Park
Positive Effects
- Provides 2,500 new homes in Newcastle where population is very high
- Will have 80 hectares of commercial development which could provide thousands of jobs
- Is adjacent to A1 and therefore has easy acesses to airports and other transport
- Scheme will slow down the net loss of 1.500 people per year who migrate from Newcastle due to job shortages
Negative Effects
- These properties are priced very high and are well beyond the average wage of people in Newcastle
- Traffic volumes would increase in city centre which could cause huge environmental problems such as air pollution
- Will have an impact on Red squirrels who are endangered aswell as the deer population which inhabit these areas
Los Angeles - Developed Megacity
Location -South west of the United States in the State of California
Population
- Tends to be gender balance, roughly equal number of males and females
- Ageing population in many areas as natural increase is lower as residents work and therfore extend marriage and children till later on in life
- Residents tend to be either wealthy or have average income
- Wealth tends to be concentrated in the inner city or suburb areas
Economy
- Hollywood based here
- Lots of TNC's e.g. Fox
- University educated graduates
- Tourism
- Finance sector -Tertiary and Quaternary sector
Lagos - Developing Megacity
Population
- Youthful population, most under 25 years as many residents are young migrants
- Often, men outnumber women as they tend to migrate first
- Many are economically active migrants who have come to city to find work
- Population of 30,000 to 21.5 million
Economy
- Secondary employment such as manufacturing in factories
- Lots of people working in docks/ports which shows export is important
- 'Informal jobs' - job where person earning money does not pay tax. This is illegal and a prevalent sector due to unskilled people
- 10,000 people come per week to find work
- Wages have dropped due to high demand of jobs leading to 23% unemployment
London's Eco-footprint (1)
Water
Each person in London consumes 161 litres of water per day .This consumption is far greater than supply leading to overabstraction of groundwater. Water also has to be transferred which increases the cost and risks the supply .London also has desalination plants which is costly and further increases costs for Londoners
Waste
London generates about 20 million tonnes of waste each year much of which is still buried in landfill sites. This waste has to be removed from city which costed London in 2011 £260 million and by 2014 it has increased to £280 million. Some waste leaks into rivers (leaching) and contaminates water supply which cause euthropication
BedZed - Sustainable Housing Development
Bedzed is trying to reduce waste generation through:
- Re-using waste
- Recycling components in draws which encourages people to recycle
- Recycle water by using water filter which can be reused for toilet flushing
- Building materials used are recycable
- Conserving Heat
- Layers of thick insulated walls placed to keep heat inside which reduces heating demand by 90%
- Faces towards south to attract sunlight through retro-fitted solar pannels which attract sunlight heating up homes
- Sustainable Transport
- Bike zones to promote people to cycle when possible
- Reduce car use as closer to good public transport
- Car sharing scheme some of which are hybrid cars
London's Sustainable Transport
Hybrid Buses
- Fuel efficient as uses the latest green diesel-electric hybrid technology
- Reduces carbon dioxide levels by 30% and reduces noise and air pollution
- Very expensive and battery does not last very long so has to be replaced from time to time
Low Emission Zone
- Encourages the most polluting heavy vehicles driving into capital city to become cleaner by allowing vehicles that meet minimum emissions or making heavy vehicles pay congestion charge
- Reduces traffic pollution particularly in residential areas which improves health.Small businesses can't afford delivery charge which could make them shut down.
'Boris Bikes'
- Promotes the use of bikes by displaying 6000 bikes for hire for the use of residents for specific amounts of time and can be accessed from 700 docking stations
Mexico City
The growth of the Informal Economy
- Cause
- 5.8% unemployment rate in Mexico mostly people who lost their job in industry.Some people moved to Mexico city in hopes of finding a job but were unsucessful and ending up working in the informal econom. 1000 people move to city with little qualification so have to do informal work
- Informal Economy in Mexico City
- 13.5 million people working in the informal sector
- Jobs include : street food markets, street vendor, window washing, street performers
- Some people working in informal economy to fund for education
- Impacts
- Only 1/3 of population economically active
- Government is not able to improve economy as is losing money as less tax payers
- Often goods sold by people working in this sector is stolen which increases robberies in Mexico and can lead to illegal jobs such as stealing
- Government do not have enough money to to spend on healthcare and infrastructure
Curitiba, Brazil
Recycling
- Encourages people to bring waste to recycle plants where they can be exchanged for food or travel cards
- Socail- more jobs availabe, poorer people save money from using green exchange
- Environmental- less factories to create new materials, less landfill sites across town as less waste generated as a result of exchange making towns safer and more attractive
- Economic- recycling plant employs disabled people, alcoholics and the homeless given a second change at life through these job oppurtunities
Masdar - Planned Sustainable City Project
Aims
- Ensuring a low carbon footprint during and after its construction
- Educating three quarters of the 40,000 residents with 5 hours of sustainability education
- Reducing waste through encouraging changes in behaviour and regulating materials which can be present in the city
How will eco-footprint be reduced
- Most of transport will be provided by rapid transit system which will leave the streets free for pedestrians. Energy will be powered by solar, wind, geothermal and hydrogen sources
- To reduce the need for air conditioning, wind towers will be used to draw colder air into homes
Problems
- Building Masdar city is hugely expensive (up to $20 million dollars). 15 years delayed
- Scarce water is being used to cool the air in the dessert which could eventually run out
Rio de Janeiro - Self-help Scheme
Benefits
- Some people living in the favellas have experience with building and construction so the Government will provide building materials such as bricks to improve favellas
- This has helped improve the areas and has resulted in some people setting up businesses such as shops which has allowed people to start earning money
- This self-help scheme has also contributed to improvements in public facilities in favellas such as schooling as now have access to clean water and electricity
Disadvantages
- Drug crimes and disease are still a major problem in the area
- Authorities cannot keep up with the level of migration to these favellas per year
Curitiba, Brazil (2)
Housing
- Moved away from conventional large housing complexes to smaller and better integrated ones due to high demand for housing as a result of increase of people moving into the city . These housing programmes are designed to meet the needs of specific communities
- Socail - People of all income bracket are able to afford homes, schools and day-care facilities are always localised
- Environmental - Housing is built with green space for people to enjoy, recycling facilties inbuilt
- Economic - Housing is cheap and affordable, private developers help fund housing
The NE & The SE (2)
South East (Surrey, Kent, Hampshire District)
- UK's most densely populated region with 8.7 people resident there
- London salaries boost average household earnings in this region because many people commute as this area in the UK is the most expensive for housing and land
- Has many job oppurtunities. Iin 2011, its unemployment rate was 6.3%
- Contains two of the UK's largest ports (Southampton and Dover) which provides thousands of jobs
- Has many significant employers in the knowledge economy. For example many top IT companies (Microsoft) are located in M4 corridor
- Average household income in UK - £35,200 which is 35% higher than NE
- Many well paid tertiary jobs and public sector jobs which give better promotion oppurtunities
London's Eco-footprint (2)
Transport
Road traffic contributes to 22% of London's carbon dioxide ouput which contributes hugely to the enhanced greenhouse effect. 41% of the nitrogen dioxide pollution in London comes from exhaust fumes. These figures suggests how transport in London increases our carbon footprint due to increase in air and noise pollution
Energy
As population increases there is more energy demand. 92% of London's energy is generated by burning fossil fuels which leads to the enhanced greenhouse effect. To countinue to compete at a world level and generate money, London needs to run 24 hours a day. Opening buildings up for 24 hours a day consumes more energy which further increases our demand.
Containerisation (2)
Internet
- This has helped to increase global trade as goods can instantly be brought online from your home making it easier to buy goods from other countries
TNC's
- Some TNC's such as Sinopec have invested large amounts of capital in different parts of the world, opening up trade with some of the poorest parts of the world like Sub Saharan Africa
Related discussions on The Student Room
- Geography mock on monday: Help »
- Quantitative Skills for Biology »
- Competition of Organisms »
- Music and language »
- Do degree based optional modules matter ? »
- What criteria does an EPQ have to fit? »
- essay question - sociology »
- what is life at eton college / harrow / winchester / tonbridge etc like? »
- AQA A Level Geography Paper 2 (7037/2) - 6th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Elective Modules at Bath Chemical Engineering »
Comments
No comments have yet been made