Cells break down food to release energy, this happens in the process called cellular respiration or respiration.
The released energy is used for muscel contraction, active transport, building up large molecules and cell division.
Aerobic respiration - oxygen is used to oxidise food. Carbon and water are released as waste products:
Glucose + Oxygen --> Carbon Dioxide + Water (+Energy)
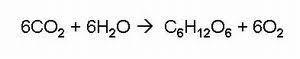
Anaerobic respiration - when no oxygen is available, Glucose is not completely broken down and less energy is released. In yeast the waste products are Ethanol and Carbon Dioxide. In animal cells the waste product is Lactic Acid
Glucose --> Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide (+Some Energy)
Glucose --> Lactic Acid (+Some Energy)
Comments
No comments have yet been made