Biology year 10
- Created by: Katie19942002
- Created on: 21-04-17 14:03
Metabolism
All the chemical reactions that happen in our body
- Exercise speeds it up
- enzymes control (proteins)
- don't eat > slows down
Catabolism > reactions that break large mollecules down to small
Exercise
During exercise:
- Our muscles contract more
- We respire more
- We need more oxygen & glucose
- We breath depper & faster
- Our heart beats faster to deliver more oxygen
Oxygen debt
- Anerobic respiration > builds up lactic acid (waste product)
- after exercise pay off using oxygen > oxidises the lactic acid
Communicable > can be passed on through bodily fluids
Exercise (continued)
Contollable risk factores of lifestyle diseases:
- your diet & weight
- levels of physical activity
- smnoking and alcahol abuse
Uncontrollable:
- age
- race
- gender
- heredity
Lifestyle dieses:
- Cardiovascular, diabetes, stroke, cancer, depression
Communicable and non-communicable diseases
Communicable diseases are caused by pathogens > can be passed on
Non-communicable diseases can be caused by genetics, lifestyle habits & enviroment
Auto-immune > body's own immune system attacks itself
Immune diffeciancy > a lack of immune system
Cancer
- Cells divide uncontrollably
- 250 different tissues > 250 different types of cancer
carciogenic > cancer causing
Eg. ionising radiation, sun exposure, viruses, diet, genetics, alcahol
Diabetes (type 2)
Type 2 > The inability to respond to insulin
Causes :
- smoking
- high blood pressure
- high fat & cholestral
- overweight
- in-active lifestyle
Type 1 > the inabilty to produce insulin
Health > mental & physical well being
Stroke > blood clot or burst blood vessel (deprives brain of oxygen)
Depression
- low mood
- aversion to activity
- anxiety
- guilt
- irratable
- restless
Can be triggered by lifestyle & events
Preventions:
- healthy eating > releases endorphens
- exercise
- weightloss (to certain extent)
- regular sleep
- meditation
- healthy relationships
BMI & cholesteral
- Personal helathy weight
- BMI = mass/height (m)2
Cholesteral > stored in cells in wall of artery
- makes it harder for blood to flow > heart must beat harder
High Density Lipoprotein > good : )
Low Density Lipoprotein > bad : (
Causes of immune dificiences:
- viruses
- drugs
- trauma
- malnutrion
- parasites
- genetics
BMI & cholesteral
- Personal helathy weight
- BMI = mass/height (m)2
Cholesteral > stored in cells in wall of artery
- makes it harder for blood to flow > heart must beat harder
High Density Lipoprotein > good : )
Low Density Lipoprotein > bad : (
Causes of immune dificiences:
- viruses
- drugs
- trauma
- malnutrion
- parasites
- genetics
Diseases, Benign & malignant cancers
Benign tumours > slow growing & don't spread
Malignant tumours > shed cells causing secondary tumours
Pathogens > disease casuing organisms
Diseases & viruses
Transmission diseases > casued by pathogens (disease causing organisms)
Bacterial diseases > killed by antibodies (water enter cells via osmosis > swell & burst)
Viruses > protein coat ( capsid) with genetic material enclosed
> don't respire, hide in other cells, antibodies uneffective
Fungi > cell wall never made of cellulose
Protoctists> have an nucleus, extremely varied cells (hard to find drugs to kill without side effects)
Respiration
- Takes place in every living cell in body
- Aerobic respiration > uses oxygen
- Anerobic respiration produces lactic acid (oxygen debt)
- Aerobic respiration produces more energy
- Chemical reaction > takes place in cytoplasm
- Oxygen debt > must oxidise the lactic acid
- Fungi anerobically respire > produces ethanol & CO2
- Carbohydrates are stored as glycogen in muscles
Measles
Transmission:
- Contained in droplets from nose & mouth (live for 2 hours)
- Transmitted by breathing in, toching them
Symptoms:
- Appear 10 days after infection
- Cold like symptoms, red eyes, sensitive to light
- High temperature, small grey spots (inside of cheek), blotchy rash
Treatment:
- Paracetamol to break fever
- Close curtains to reduce light, can potentially kill
Prevention > MMR vaccine
HIV
Transmission:
- Passed on through bodily fluids eg. intercourse, needle, mother to baby
Symptoms:
- Fever, sore throat, body rash, tiredness, joint & muscle ache
- Attacks white blood cells > lowered immunity so people often die of infections
Tretament:
- Antiretroviral work > stops viruse replicating
- Allows immune system to repair
Prevention > don't share needles, use condom etc.
Gonorrhoea
Transmission:
- Sexually transmitted via bacteria
Symptoms:
- Thick green/yellow discharge from vagina or penis
- Pain when urinating
- Bleeding between perios (women)
Treatment:
- Single antibiotic injection & tablet (starting to resist)
Prevention > condoms etc.
Salmonella
Transmission:
- Eating an infected item (lives in gut of many farm animals)
- Affects meat, eggs, poultry & meat
- Can occure if raw & cooked foods stored together
Symptoms:
- Diarrhoea, stomach cramps, vomitting, fever
- Can kill
Treatment:
- Severe cases treated with antibiotics
- Drink lots of fluids (may be given rehydration solution)
Prevention > wash hands regularly, especially after loo, touching animals or food
Tobacco Mosaic
Transmision:
- Conatnimated leaf touching other
- Contaminated tool
Symptoms:
- leaf curling
- yellowing of plants.
No treatment > infected plants must be removed
Prevention:
- Avoiding damp conditions & tobacco around plants
Malaria
Transmission:
- mosquito bites infected person
- parasites multiply in gut
- when bites another person > disease transmitted
Symptoms:
- recurring fever, delirious
- can result in death
Malaria tablets, mosquito nets etc.
Some drugs effective > parasite can be resistant
Culturing fungi from leaves
Method:
- Disinfect bench with ethanol & wait to evaporate
- Unscrew heated algar jelly (60.), flame neck of bottle
- Pour into petri dish
- Replace lid & swirl petri dish to spread
- Leave to set
- Press leaf on to gel
- Attach lid with tape (ensure oxygen can still enter)
- Turn dish upside down
- Incubate at 26.C (so pathogens don't grow)
- Single cell fungi (yeast) had grown
- Bacteria also grew
Immune deficiences
Viruses: (including HIV)
- Attack white blood cells which fight disease
Drugs:
- Chemotherapy drugs can damage immune system
- transplant patients take anti-rejection drugs > weaken imune system to prevent rejection
Trauma: (including major surgery)
- Spleen (can live without but will slowly deterioate > involved with immune system) may be damaged & removed
Malnutrition: (including lack of vitamins)
- Proteins > needed to make antibodies
- Vitamins > needed by immune system
Immune deficiences (continued)
Malnutrition: (including lack of vitamins)
- Proteins > needed to make antibodies
- Vitamins > needed by immune system
Parasites:
- Reduce the immune system's response > prevents host from killing them
Genetics:
- Some people born with weaker immune system
Human defence system
Pathogens eneter by:
- Insects/mammal bites
- Inhaling (common cold)
- Exchanging bodily fluids
- Contaminated food/water
- Scratches or punctures
How does body defend?
Eyes:
- tears wash out pathogens
- contain an enzyme (lysozyme) to kill bacteria
`Human defence system (continued)
Skin:
- Dry & dead (on surface) > wet skin =fungi eg. athlets foot
- Dead > viruses reproduce in living cells
Stomach:
- Hydrochloric acid kills micrbes
Blood clotting:
- Seals wound
- Trap bacteria in clot
Airways:
- Produce mucus to trp microbes
- Ciliated ethilium waft mucus out of lungs
White blood cells
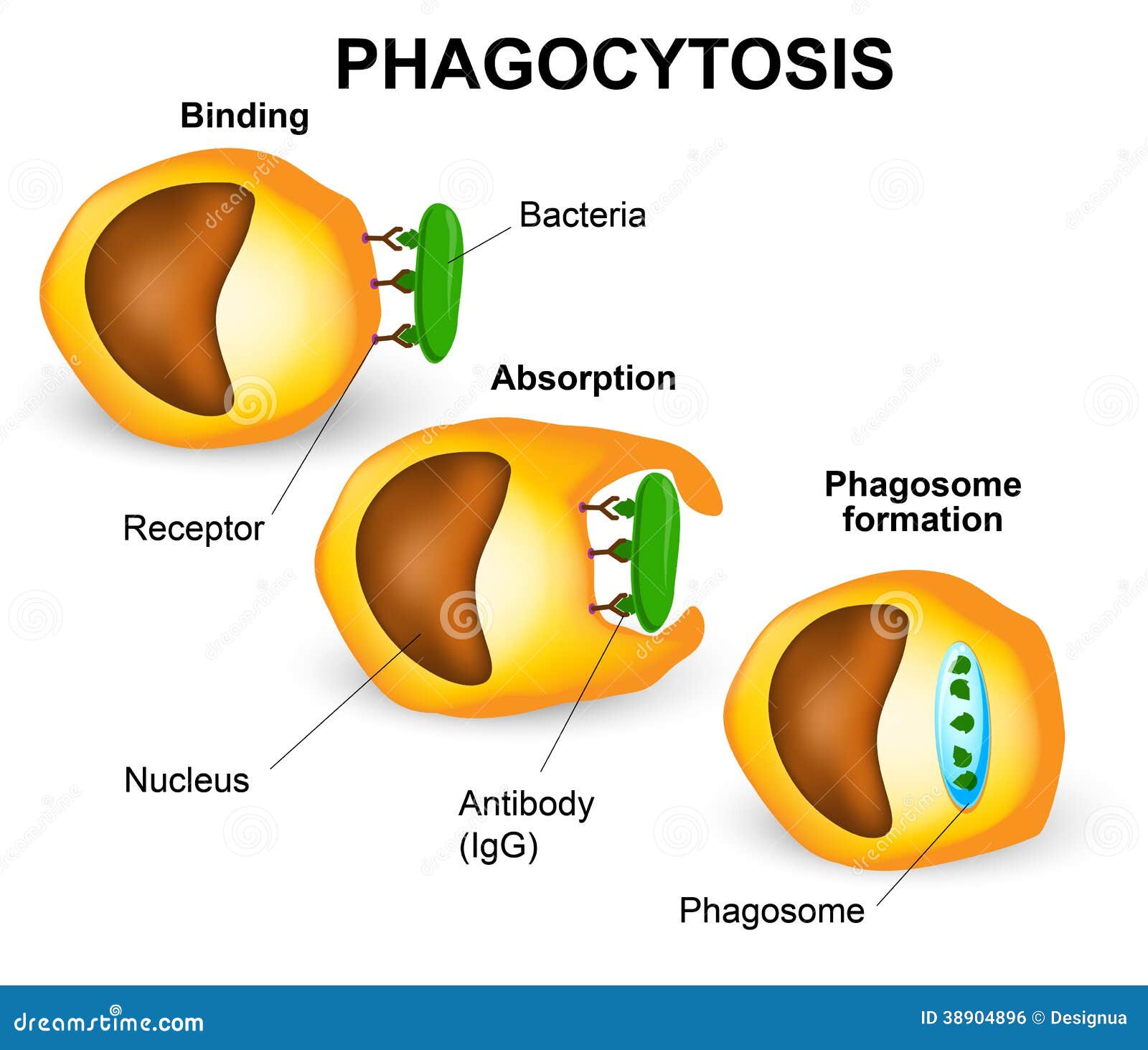
Phagocytes = first line of defence
- Don't identify what cell is
- Identifies it as diferent
Antibodies & antigens
Antigens:
- Chemical substance found in/on cell
- When recognised > triggers immune response
Antibodies:
- Produced by lymphocytes
- Can only recognise one type of antigen
Immunity
Few types of lymphocytes > produce few types of of antibodies
If a foreign antigen gets into our body:
- Relevant antibody recognises & sticks to
- Sends signal to lymphocyte to multiply > produce more antibodies
- This takes time > pathogen multiplies making you ill
Once disease passed:
- Some lyphocytes remain as memory cells
- If pathogen enters again cells rapidy reproduce (don't get ill)
- Now immune
Vaccination
Patient is exposed (injection, drop on tongue, nose spray) of inactive strain of pathogen
Immune system response:
- Antibodies which recognise bind
- Causes lymphocytes to divide via mitosis
- 'Fights' of disease
After:
- Some of the white blood cells remain (memory cells)
- Next time same pathogen invades > rapid response
Vaccination (continued)
Why can you get flu more than once?
- More than one strain
- Strain 1 antibody can't recognise strain 2 etc.
Herd immunity
- High portion vaccinated > disease can't spread
- Infected person won't find another un-vaccinated person
- Dosent always work > often un-protected pockets
- could in theory still spread > movement etc.
MMR vaccination
- 90's doctor made thpught there was a link between MMR vaccine & autism
- Results were on small scale so unreliable (was only a gp)
- Vaccination given at same time as most children diagnosed for autism
Antibiotics
Discovered by Alaxender Flemming
What is an antbiotic:
- Works within body to kill & stop spread of bacteria
- Work by damaging cell wall
- Water enters cell via osmosis > cells explode
Don't affect viruses as don't damage our own cells
Antibiotic resistance
How do antibiotics work?
- prevent from making new cell wall
- water enters via osmosis > swell & burst
Antibiotics cannot cure viruses becuase:
- viruses don't have cell wall
- live inside our own cells (not affected by antibiotic)
Antibiotic resistance (continued)
Reasons for resistance:
- random mutations can result is resistance
- if antibiotic dosen't kill ones that survive = resistant
- people might not finish course of antibiotics or use too often
Developing medicine
Must be:
- effective > prevent,cure or relieve symptoms
- safe > side effects should be mild
- stable > must last over time & keep in normal conditions
- successfully absorbed & exerted by body
Can take up to 12 years & £550 million to £1 billion to make
Monoclonal antibodies
Uses:
- pregnancy tests
- disease diagnosis
- treating disease
Treating cancer:
- Some cancers have specific antigens on surface
- make specific monoclonal antibodies > stick to cancer cell
- once produced attach radio-active element
- cancer cells recieve high dose of radiation
- healthy cells not affected >reduces side effects of radio/chemotherapy
Monoclonal antibodies (continued)
Identifying chemicals:
- can attach fluorescent chemicals to antibodies
- put them into body & see where it ends up
Measuring hormone levels:
- take a sample of blood
- use antibodies to 'diagnose' amount
Polyclonal antibody > inject large antigen into animal, differnt antibodies recognis it > lots of different antibodies stick to it
Monoclonal antibodies (continued)
Identifying chemicals:
- can attach fluorescent chemicals to antibodies
- put them into body & see where it ends up
Measuring hormone levels:
- take a sample of blood
- use antibodies to 'diagnose' amount
Polyclonal antibody > inject large antigen into animal, differnt antibodies recognis it > lots of different antibodies stick to it
Monoclonal antibodies (continued)
Identifying chemicals:
- can attach fluorescent chemicals to antibodies
- put them into body & see where it ends up
Measuring hormone levels:
- take a sample of blood
- use antibodies to 'diagnose' amount
Polyclonal antibody > inject large antigen into animal, differnt antibodies recognis it > lots of different antibodies stick to it
Monoclonal antibodies (continued)
Monoclonal antibody >
an antibody produced by a single clone of cells or cell line and consisting of identical antibody molecules (made in labs) Pregnancy tests: - test changes colour when hormone found in pregnant women urine bind to antibodies with coloured head attached
antibiotic resistance
Reasons:
- overuse of antibiotics
- mot finishing course of antibiotics
In this country antibiotics are subscription only medicine
The bacteria that survives if a course is not finished will become resistant
In some countries cattle are fed antibiotics for growth & 'just in case' in cramped conditions
Eating that meat means that we are eating already resistant bacteria
Developing new drugs (thalidomide)
Thalidomide:
- developed as a sleeping pill 1950's
- started using to relieve morming sickness (not tested for this use)
- affected growth of babies limbs
- Dr. kelsey was in charge of reviewing for use in America
- pressed for more research before allowing
- kept of market for year by which time connections had been made
Developing new medicines
Has to be:
- effective
- safe
- stable
- taken into & out of body successfully
How are new drugs tested?
- researchers target a disease
- make lots of new drugs & test them on > cells, tissues, whole organs
Developing new medicines
Has to be:
- effective
- safe
- stable
- taken into & out of body successfully
How are new drugs tested?
- researchers target a disease
- make lots of new drugs & test them on > cells, tissues, whole organs (check whether they are toxic, do job etc.)
Developing new medicines (continued)
- drug is then tested on animlas to see if it works & possible side effects
- then given to healthy people in low doses
- bigger clinical processes take place to find correct dosage
- it can then be prescribed
Placebos
- A treatment which appears to be the same as the real treatmet but without the accurate ingrediant
- given to check that affects or not 'phycological'
- will often be given a substitute
In drug trials the treatment is double-blind meaning that the patient or the doctor don't know which treatment is being given
Homeostasis
Have to keep body at optimum temperature for enzymes
Too hot:
- blood vessels dilate > vascodilation
- hair lays flat so dosen't trap heat as well
- body sweats > when evaporates takes away heat
Too cold:
- blood vessels contract > vascoconstriction
- hair stands up to trap heat better
nervous system
stimulus eg. sound ........ receptor eg. hair in cochlea
receptor > sensory neurone > central nervous system > motor neurone > effectors
Central nervous system > brain & spine
reflex arc
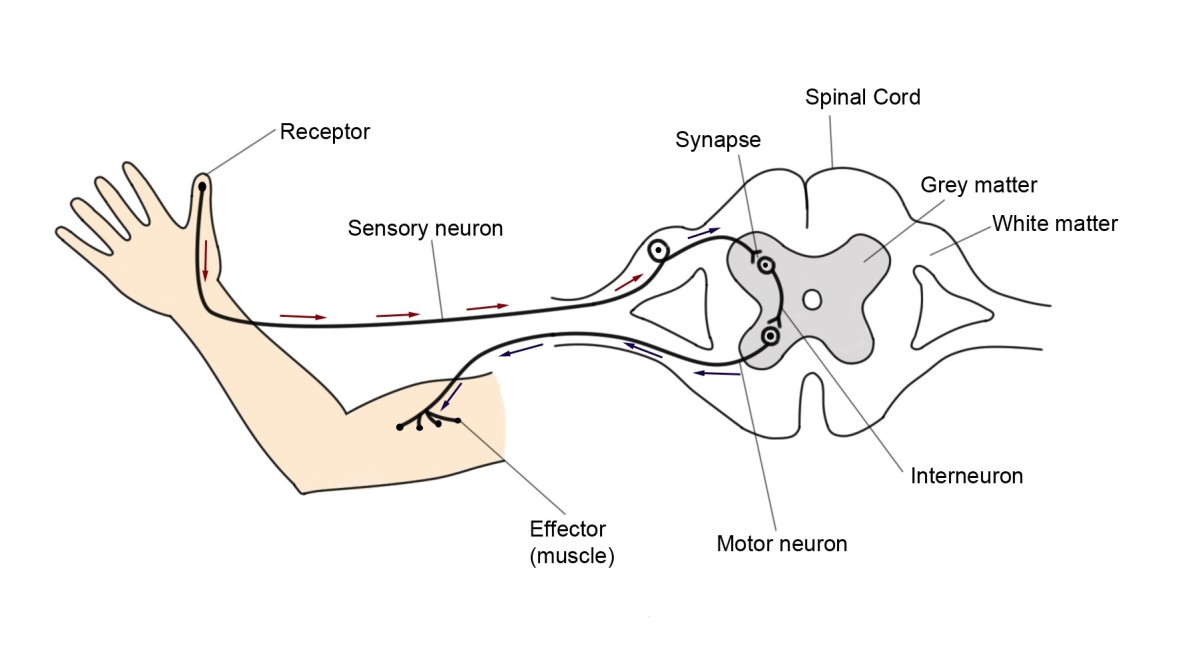
reflexes
Reflexes > automatics responses which dont require conscious thought
Avoids serious injury
myelin sheath > coats neurones allowing electrical signal to travel faster (insulates)
nerve = bunch of neurones
synapses
- neurones send electrical signals along axon
- when signal gets to then end chemical messages (neurotransmitters ) diffuse across the gap
- gap is known as synpase
- the signal then carries on through to the next neurone
The brain
Cerebellum > co-ordinates movement & balence (controls volentary tasks eg. walking)
Medulla > connection between brain & spine (controls involentary tasks eg. breathing)
Cerebral cortex > four parts - conscioussness, memory, intelligence & language
The brain (diagram)
the Eye
Iris > contracts to control size of pupil & amount of light entering
Lens > focuses light on retina
Retina > detects light intensity
Optic nerve > sends electrical signals to brain
Fovea > parts of retina (sees detail & colour)
eye labelled diagram
Common eye problems
- The cornea & lens bends light to focus on to retina
Object far away > lens is stretched thin (small angle)
> ciliary muscles pull lens
Object close > lens is fat (large angle)
> suspensory ligaments contract
Common eye problems (continued)
Long sighted (hyperopia):
- fixed with a convex lens
- light dosne't focus soon enough when object is close
- far away things are fine
Short sighted (myopia):
- fixed with concave lens
- light focuses too soon when object is far away
- close up things are fine
Eye ray diagrams
Hyperopia (long sighted)
Myopia (short sighted)
Hormone
A chemical message
Endocrine gland > hormone secreting gland (secrets directly in to blood)
Oestrogen/estrogen > causes lining of uterus to build up (made in ovary)
Progesterone > maintains lining of uterus and is used if pregnant (made in ovary)
FSH > stimulates ripening of egg (made in pivitary gland)
LH > stimulates the relase of the egg -ovulation (made in pivitary gland)
hormone levels
contraception
combined pill > prevents ovaries from releasing egg, thickens mucus in neck of womb, thins lining of womb
4 types of pill all slightly different but do simular things
Implant (upper arm) > can't be removed lasts 3 years, slowly releases progesteron, tickens mucus, thins lining
Injection > lasts 8-13 weeks, takes 1 year for full fertility to come back, releases progesteron, thickens, thins lining
Barrier methods offer protection from STD's > hormonal dosen't
contraception (continued)
IUD (implant in uterus) > stops implantation of egg (moral issues)
Rhythm method > abstain from intercourse during fertile parts of cyle (very unreliable)
Hormones to increase fertility
Artificial FSH can be given to increase ovulation > stimulates eggs to mature & production of estrogen
IVF
- Women is given high levels of fsh so many eggs mature
- On the day eggs are removed women is given LH
- Needle & camera are inserted through abdomen to release around 12 eggs
- eggs are fertilised in petri dish
- fertillise into embryos
- 1-3 healthy embryos selected
- women is given hormones to cause lining to form & embryos inserted back in
Hormones to increase fertility (continued)
IVF is very expensive & not always effective
Moral issues:
- some embryos killed
- can choose babies' looks if using donor
- too many eggs can be fertilised hightening risk of baby dieing
Plant hormones
Response to light > phototropism
Response to gravity > gravitropism/geotropism
Auxin:
- Slows growth in root
- Quickens growth in stem
- Can be used as weed killers & rooting powders
Plant hormones (continued)
Ethene:
- controls cell divison & ripening of fruits
- used in food industry to control ripening in transport & storage
Gibberellins:
- stop seeds germinating
- promote flowering
- increase fruit size
Saviour siblings
A child perpously conceived through IVF as a potential source of donor organs or cells for an existing sibling with a life threatening medical issue.
Problems:
- child does not to choose to become donor so do not have right to take them
- potentially damaging for a child to know they're existence is for anothers purpose
Photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water > glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H20 > C6H12O6 + 6O2
How plants use glucose
- strengthening cell walls > build up glucose supplies then change them in to more complex carbohydrates such as cellulose then use to strengthen walls
- storing > some glucose is changed into starch for storage in roots, tubers & seeds (glucose is soluble in water whereas startch isn't so better to store)
- to make amino acids > by combining sugars with nitrate ions & other mineral ions from soil. Amino acids are buit up into proteins for use in cells (this requirs enrgy from respiration)
- making fats & oils > use glucose from photosynthesis& energy from respiration to build up fats & oils. Used in cells as energy stores & to strengthen cell walls.
Plants often store energy in seeds so they have lots of energy as they germinate
How plants use glucose (continued)
Plants respire constantly!
1. releasing energy from glucose for respiration
2. complex carbohydrates - storge of starch (found in leaves short term so plant can respir during night kept in roots, tubers, bulbs & seeds long term)
- structurally used as cellulose to strenghthen cell walls
Nb. starch & cellulose are made from thousands of glucose molecules joined together
3. amino acids for protein (made by combining carbohydrates with nitrate ions from soil)
4. fats & oils (synthesing lipids)
5. other carbon containg compounds eg. vitamins, DNA
Environment
community- total number of individuals in an ecosystem
population - total number of an induvidual species in a given area at a given time
ecosystem - the living & non-living total of an area eg. pH
habitat - the space where an induvidual lives
abundance - how many induviduals present
distribution - the place/toal area that a population lives
How do plants protect themselves from disease
1. anti-bacteriall chemicals eg. mint, witch hazel, tea tree
Nb. plants do not have white blood cells or antibodies but instead produce substances
2. defence systems (bark, waxy cuticles, thorns)
3. anti-microbial chemicals, enzymes & proteins
If a plant is damadged it can seal the gap with sap or resin
Cellulose in the cell wall help fight against invasion
How do plants protect themselves from disease (con
If a plant finds the presence of a pathogen it can:
- close their stomata
- activate a hypersensitive result
- activate endophyte assisstance
hypersensitive result > killing cells in pathogen surrunding so it can't spread or survive
endophyte assisstance > roots releasing chemicals that attract beneficial bacteria to fight infection
Biodiversity
Biodiversity > a measure of the variety of different species of organisms on Earth or within a particular ecosystem (cruical for stability)
If there is a change, biodiversity ensures everything is not wiped out
ie. clown fish feed on many different anemies so that if one breed is wiped out the clown fish won't die
Biodiversity
Biodiversity > a measure of the variety of different species of organisms on Earth or within a particular ecosystem (cruical for stability)
If there is a change, biodiversity ensures everything is not wiped out
ie. clown fish feed on many different anemies so that if one breed is wiped out the clown fish won't die
Biodiversity
Biodiversity > a measure of the variety of different species of organisms on Earth or within a particular ecosystem (cruical for stability)
If there is a change, biodiversity ensures everything is not wiped out
ie. clown fish feed on many different anemies so that if one breed is wiped out the clown fish won't die
Why are we now expected to live for longer
- medicine
- more peaceful resolutions to large scale combat
- better prevention/help for natural disasters
- protection due to law/order
- improved hygeine
- vaccines
- working conditions improved
Due to this our human population is growing at an exponential rate
Global warming
Temp of earth is balence between energy it gets from sun & energy it radiates back to space
Gases in the atmosphere act as insulating layers > absorb most of the energy that wpould normally go to space and re-direct it in all directions including earth
This increases the earth's temperature
Consequences:
- rise in sea level
- change sin species distribution
- changes in migration pattern
- reduction in biodiversity
Pollution in water
Pollution in water (continued)
Bioaccumaltion
-
Small amounts of toxic substances - often from human activity - are taken up by plants.
-
These plants are eaten by primary consumers.
-
The primary consumers are eaten by secondary consumers, and the secondary consumers are eaten by higher level consumers.
-
At each stage (trophic level) of the food chain, harmless substances are excreted but the toxins remain in the tissues of the organisms - so the concentration of toxin becomes most concentrated in the body tissues of the animals at the top of the food chain.
Acid rain
Acid rain effects the waxy layer on trees' leaves making it more difficult for them to absorb the minerals they need to grow
Acidic gases such as sulphur dioxide are produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas burn. Sulfur dioxide dissolves in the clouds and causes acid rain. This damages buildings, trees and harms life in rivers and lakes. It also causes chemical weathering of rocks to happen much faster than normal.
Deforestation consequences
-
It reduces the rate at which carbon dioxide is absorbed and ‘locked away’ in the plant biomass by photosynthesis, as there are fewer trees.
-
As timber is burnt to clear space, it increases the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. The remaining parts of the tree (eg the roots) are then decomposed by microorganisms. This adds further carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and so contributes to global warming.
-
Forest habitats are destroyed and biodiversity is reduced.
-
Cattle are often reared on the land, producing methane. Methane, a greenhouse gas, contributes more to global warming than carbon dioxide.
Peat
Peat is formed in waterlogged, acidic fens and bogs over thousands of years by the growth of mosses and other plants, which absorb and ‘lock away’ carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. When the moss dies, the waterlogged bog provides anaerobic conditions which, together with the acidity of the bog, prevent the total decomposition of the moss. It accumulates in the bogs in a partially-decomposed state, forming peat.
Peat bogs cover nearly 2-3% of the Earth’s surface and are an important carbon sink,containing more ‘locked-away’ carbon than the Earth’s forests.
Carbon sink >absorbs more carbon than it releases
Related discussions on The Student Room
- MRes Programmes - Faculty of Medical Sciences 2022 »
- Uni decision »
- Biological sciences choosing universities »
- What life science degree should I do? »
- What is actually studied in a pharmacy degree? »
- Psychology or Psychiatry? »
- Can I go into biochem or work in the medical field with these alevels? »
- Why study Biomedical Science at Bradford? Thread »
- My experience studying MPharmacy »
- Can I still be a vet if I don't take A level Chemistry? »
Comments
No comments have yet been made