Assessing Internationalisation
- Created by: Leary103
- Created on: 16-01-21 12:03
International markets
Reasons for targeting, operating and trading in an international market:
- Avoiding the risk of operating in a single market
- Taking advantage of economies of scale and the experience curve
- Boosting profitability
- Competing against international firms in order to safeguard domestic markets
- Increasing market share and achieving business growth
- Better serving key customers located abroad
- Developing market knowledge and expertise
- Making a competitive move
- Taking advantage of government incentinves
Factors influencing the attractiveness of internat
- The size of a potential market and its expected growth
- The accessibility of the international market
- Compatibility or alignment of the market
- Availability of financial and other resources
- The competitive environment
- The external environment (PESTLE factors)
Reasons for off-shoring
Off-shoring: where companies outsource or subcontract business activities overseas, largely because labour and other production costs are much cheaper there; also known as outsourcing off-shore
- Many businesses decide to produce more, and more of their resources are abroad (generally, costs are cheaper)
- Lack of investment in manufacturing in the UK
- Availability of low-paid, unskilled workers
- Multinational companies may already have capacity and capability abroad and may prefer to improve their efficiency by utilising that rather than producing in the UK
- Can be far easier to establish manufacturing operations abroad
- Off-shoring production facilities can allow business leaders to focus on what they do best
- Take advantage of free-trade areas
Problems with off-shoring
- Additional business risks associated with the transition period, political instability, and natural disasters, which can disrupt business continuity
- Increased additional costs, including managing the transition abroad, ongoing management and supervision costs, transport, delivery and insurance costs
- off-shoring to developing countries affect a company's image and its reputation for CSR
- Currency fluctuations can affect profit margins
- Difficulties in controlling the quality of goods or services provided
- Communication, including language differences, particularly for highly technical products
- Logistics, including transportation, delays in deliveries, the responsiveness of suppliers and their ability to get products to market quickly enough
Reasons for re-shoring
Re-shoring: the reverse of off-shoring; the transfer of business operations back to the country of origin; also known as on-shoring
- Shifting customer preferences
- Desire to respond more quickly to consumer preferences - create a competitive advantage
- Reduction in the wage gap in emerging economies
- Fluctuating exchange rates
- Difficulties in dealing with changing international transport costs, import duties, potential transport disruptions and supply chain risks
- Desire to improve cash flow by reducing levels of inventory that need to be held
- Desire to improve the quality of products and components
- Desire to reduce the production-to-market lead time so that companies are able to react more effectively to emand
- A desire for a solid legal framework and a predictable regulatory system
Exporting
Exporting: Goods or services produced in one country are sold in another
Advantages:
- reduces risk and little investment is required
- Speeds up entry to international markets
- Makes use of existing facilities and therefore increases economies of scale
Disadvantages:
- May face import tariffs and other trade barriers
- Incurs transport costs
- Limits access to local information about the international market, particularly in the case of indirect exporting
Licensing
Licensing: a business arrangement whereby one company gives another company permission to manufacture its goods, offer its services, and use its technology, brand or expertise for a specified fee or royalty
Advantages:
- reduces risk and little investment is required
- Speeds up entry to international markets
- Avoids import tariffs and other trade barriers
- Makes use of existing facilities and therefore increases economies of scale
Disadvantages:
- lack of control over marketing products
- Licensee may become a competitor
Alliances
Alliances: agreements between two or more companies to combine their strengths and expertise in order to undertake a mutually beneficial project - in this context, involving entry to an international market; alliances can include strategic alliances and joint ventures
Advantages:
- combines the resources and strengths of two or more companies
- potential for learning and benefiting from each other
- Less investment required than going it alone
Disadvantages:
- Can be difficult to manage
- Less control than going it alone
- A greater risk than exporting and licensing
- Partner in the alliance may become a competitor
Direct Investment
Direct Investment: the taking of a controlling ownership in a company in one country by a company based in another country; this can be via organic growth or the takeover of a foreign business; sometimes known as Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Advantages:
- greater knowledge of local markets
- opportunities to make better use of specialist skills
- retain the knowledge of products and markets within the company
Disadvantages:
- A higher level of risk than the other methods
- requires huge resources and long0term commitment
- requires well-thought-out strategy for managing local plants and resources, including overcoming cultural barriers
Multinational
Multinational: a business that operates in several countries but is managed from one (home) country; this term is often abbreviated to MNC
Bartlett and Goshal's model

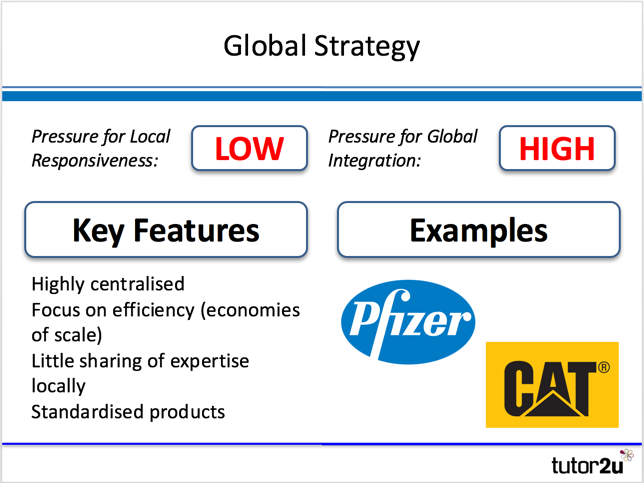
Global Strategy
Transnational Strategy

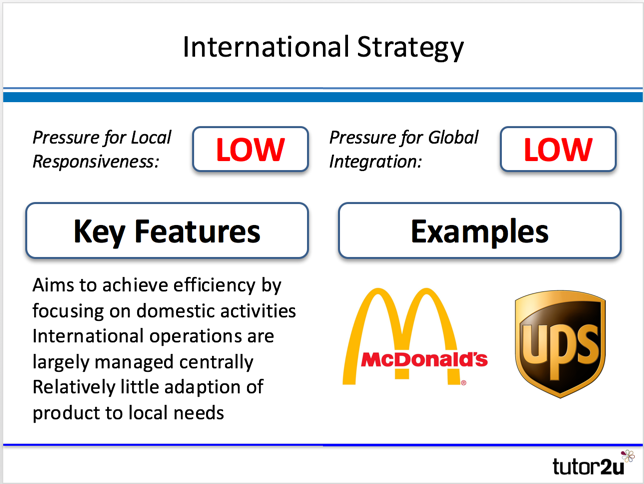
International Strategy
Multi-domestic Strategy

Related discussions on The Student Room
- Unveiling the Realm of Investment Banking »
- Answering Questions: What can a degree in Business Management lead to? »
- Can I get into investment banking with an Accounting and Finance degree? »
- Uni revision stratgergies »
- AQA A Level Business Paper 3 (7132/3) - 14th June 2023 [Exam Chat] »
- Capital one case study interview »
- resitting a levels »
- Master in Public Policy | LSE »
- Could someone please help with some feedback »
- Could you give me feedback on this please »
Comments
No comments have yet been made